Table of Contents
- What is Reference Data?
- What Are Examples of Reference Data?
- What are the Different Types of Reference Data?
- Reference Data vs Master Data Management
- Benefits of Reference Data Management
- Reference Data Management Best Practices
- Why Is Reference Data Important?
- Reference Data Management Requirements
- Other Blog Posts In This Series
- Frequently Asked Questions About Reference Data
Updated January 6, 2025
If you are currently considering implementing master data management (MDM) in your organization, you may have come across the topic of reference data. In this short ‘MDM 101’ post, we explain what reference data is, how it differs from other data types and why you should care.
What is Reference Data?
Reference data is a specialized subset of master data that is used to classify and provide additional context around the data throughout the enterprise. While your core master data domains like customer, product and location data typically change infrequently, reference data can change rapidly over time.
Reference data lists exist in multiple places and are referenced by multiple domains. This includes complex hierarchies, mappings and more.
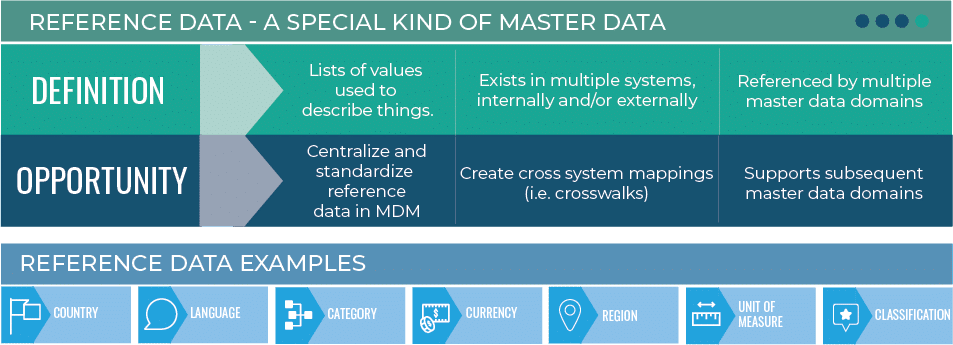
What Are Examples of Reference Data?
Common examples of reference data include:
- Postal or zip codes
- Cost centers or other financial hierarchies
- State or country abbreviations
- Internal organizational information like sales regions or departments
- Lists of languages
- Customer or marketing segments
What are the Different Types of Reference Data?
Reference data commonly falls in two distinct categories: multidomain reference data and real-time reference data.
Multidomain Reference Data
Multidomain reference data spans multiple functional areas such as finance, risk, compliance, human resources and more. It is critical to multidomain MDM because it connects multiple domains and applications together by enforcing consistent values and semantics to classify or categorize other data.
For example, a manufacturing organization can ensure own production facilities and their customers’ receiving addresses adhere to a consistent set of country and state codes to expedite order fulfillment and reduce shipping delays.
Real-time Reference Data
While not as prevalent as multidomain reference data, real-time reference data is critical for business and data users in the capital markets industry.
In this example, traders may use multidomain reference data such as an individual security’s symbol, ISIN code or other facet of the stock in order to help make sense of the real-time reference of the bids, asks and trades that happen in real time on the stock exchange.
Reference Data vs Master Data Management
Whether they are embarking on a digital transformation or other strategic initiative, some organizations decide to master their multidomain reference data before their customer, product or other master data.
By consolidating the hundreds of spreadsheets and utility tables an organization may have spread across department and regions, they are able to create a trusted golden record of their reference data that can be enforced across all other data domains. In this approach, trusted reference data is a helpful prerequisite for implementing MDM across more complex domains.
Benefits of Reference Data Management
Most successful MDM implementations manage reference data in addition to reference data to give businesses a more complete, holistic view of their enterprise data.
Reference data management allows organizations to centralize and standardize these different business lists used throughout the enterprise. While reference data is often smaller in quantity than transactional and other data, the quality of reference data has a significant impact on revenue, operational costs, reporting and governance.
Because reference data helps categorize other data throughout the organization, it affects every part of the business. Even small variations in reference data across domains or source systems can lead to significant data quality challenges later.
Benefits of managing reference data include:
- Reducing costs: By centrally managing and storing reference data in the MDM hub, organizations eliminate the costs of storing and maintaining reference tables in other systems.
- Streamlining updates: Data stewards can easily make updates to reference data in the MDM platform and publish changes to source systems and downstream applications.
- Improving analytics & reporting: Because reference data informs and provides context around analytics and business intelligence (BI) reporting, high-quality reference data directly improves the quality of reporting and insights.
Reference Data Management Best Practices
To maintain the consistency and quality of your data across the organization, it’s important to manage your reference data effectively. Not only does this help you create trustworthy, consumable data, but it may also be necessary for certain operational MDM uses cases.
This is by no means an exhaustive list, but some reference data management best practices include:
- Formalizing the Management Process: Establish clear ownership and accountability for data stewards. This is often accomplished through a dedicated reference data management team or data governance council.
- Subscribing to External Reference Data Sources: Organizations like DAMA, ISO and Swift (for finance) publish educational resources and guidelines that serve as industry standards for various processes, including data standardization.
- Developing Policies and Procedures: Similar to the first best practice listed here, a dedicated data management team or data governance council should develop policies and procedures for how your organization works with reference data to ensure reference data remains standardized.
- Auditing and Updating: Making sure that your data works for your purposes is a crucial component of data quality, and that goes for reference data, too. It’s a good idea to revisit how your organization manages reference data at regular intervals to make sure it’s still relevant and useful.
Why Is Reference Data Important?
Though most of the processes and functions reference data supports take place behind the scenes, that doesn’t mean it’s not important. Reference data plays a vital role in strategic enterprise data initiatives by helping ensure data consistency and accuracy across various systems and processes, which can have big and sometimes unexpected consequences across the organization.
The same is true of master data in general, of course, but as a specialized kind of master data that categorizes and describes other master data, reference data has a big impact on the accuracy and trustworthiness of reporting and analytics and can even be the deciding factor between certain processes and functions working or not. Without proper management, reference data can become outdated or inconsistent, leading to significant issues such as incorrect reporting, regulatory non-compliance and operational inefficiencies or disruptions.
Real World Example
Imagine a global retail company that operates in both the United States and Latin America. In its reference data, the company categorizes Puerto Rico as part of Latin America due to shipping cost considerations. However, after merging with another retailer, they discover the new company classifies Puerto Rico within the United States to align with tax and legal frameworks.
This mismatch in reference data leads to significant issues:
- Invoice Errors: Vendors and partners receive conflicting invoices due to different tax calculations and shipping rules.
- Shipment Delays: Orders destined for Puerto Rico are routed incorrectly, leading to delays and increased costs.
- Analytics Discrepancies: Sales reports for Puerto Rico are inconsistent, making it challenging to analyze performance accurately.
By reconciling and standardizing reference data between the two companies, these issues can be resolved, ensuring trusted analytics, smooth operations and a unified business perspective.
Reference Data Management Requirements
To effectively manage reference data, organizations need a comprehensive strategy that includes several key components:
- Data governance is essential to establish policies and procedures for data stewardship and accountability.
- Data quality management ensures that reference data is accurate, complete and consistent
- Technology solutions such as master data management (MDM) systems can help automate and streamline reference data management processes
- Regular training and communication help keep all stakeholders informed and engaged in maintaining high data quality standards
Other Blog Posts In This Series
Frequently Asked Questions About Reference Data
What Is Financial Reference Data?
In finance, reference data is a type of master data (you might hear some people use the two terms interchangeably) that describes financial transactions so that they can be processed. Reference data is fundamentally the same in finance as in any other industry, but in the context of finance, it deals with codes and classifications unique to that industry.
Examples of financial reference data include:
Financial Instrument or Asset Data
Is the instrument in question a stock, bond, derivative or something else?
Examples of financial instrument or asset data include:
- Securities Master Data:
- ISIN (International Securities Identification Number)
- CUSIP (Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures)
- SEDOL (Stock Exchange Daily Official List)
- Bloomberg Tickers
- Instrument Details:
- Stock, bond or derivative details
- Issue date and maturity date
- Coupon rate, face value and yield
- Underlying asset information for derivatives
Financial Market Data
Where was the instrument traded? A stock market, a bond market, a forex market or a derivatives market?
Examples of financial market data include:
- Entity Identifiers:
- Legal Entity Identifier (LEI)
- DUNS Number (Data University Numbering System)
- Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
- Counterparty Details:
- Legal name and address
- Regulatory jurisdiction
- Industry classification (e.g., NAICS, SIC)
- Parent company and ownership structure
- Risk and Credit Data:
- Credit rating (e.g., S&P, Moody’s)
- Counterparty risk limits
- Historical default or payment data
Should I Manage Reference Data Using a Spreadsheet?
Depending on the size of the dataset you’re working with, using a spreadsheet to manage reference data might work fine, but this will quickly become impractical once you start dealing with larger volumes of data — especially when it’s scattered across multiple locations. Many organizations use a master data management tool like Profisee to manage their reference data. Using MDM for reference data management keeps teams from wasting time on manual processes in addition to improving operational efficiency and making reports and analytics more trustworthy.

Eric Melcher
Eric has spent the entirety of his 15+ year career working in the enterprise information management space. As Chief Technology Officer, Eric is responsible for all aspects of product management, development and support for Profisee’s software portfolio.