In today’s data-driven world, organizations face the challenge of managing vast volumes of data from multiple sources. Master data management (MDM) solutions, such as Profisee, offer a robust framework for addressing this challenge by unifying data to create a single, accurate and consistent view of information.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the concept of data unification, exploring its importance, key differences from traditional MDM approaches, steps involved, best practices, common challenges and how Profisee MDM can assist organizations in achieving seamless data unification.
What is Data Unification?
At its core, data unification refers to the process of integrating data from multiple sources into a single, coherent view.
This involves bringing together data from various systems, databases and applications to create a unified dataset. The goal is to resolve inconsistencies, redundancies and discrepancies in the data, providing users with a consistent and reliable view of information.
Understanding Data Unification in the Context of MDM
Data unification is a critical aspect of MDM that focuses on integrating and harmonizing data from multiple sources to create a unified dataset.
Unlike traditional MDM approaches, which primarily involve managing master data entities, data unification extends beyond master data to include all types of data across the enterprise.
While MDM encompasses various processes — including data unification — it represents a broader framework for managing master data entities comprehensively.
For example, data unification focuses on integrating and harmonizing data while MDM involves additional processes such as data governance, data quality management and data stewardship. MDM ensures that master data entities are governed, maintained and used effectively throughout their lifecycle, providing a foundation for data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency.
The Importance of Data Unification
Data unification plays a crucial role in modern data management for several reasons. For starters, having a unified view of data enables organizations to make better-informed decisions.
Deeper Insights
By consolidating data from disparate sources, businesses can gain deeper insights into their operations, customer data and market trends.
For example, a company that is growing rapidly through acquisition may accumulate considerable “technical debt” of databases, applications and systems from the new subsidiaries. To glean true enterprise-level insights, executives would need to analyze supplier relationships, raw materials costs and customer behavior across all source systems — not just those at the legacy or highest-level company.
Ability to Identify Opportunities
Armed with a holistic, unified view of their business, companies can then identify opportunities, mitigate risks and drive growth.
Specifically, customer data unification can facilitate enhanced customer experiences. By integrating customer data from various touchpoints — regardless of whether it’s a support interaction managed by one team or a marketing email managed by another — organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers’ preferences, behaviors and needs. This allows them to deliver personalized and targeted experiences, ultimately using customer data to improve satisfaction and loyalty.
Breaking Down Data Silos
Additionally, data unification helps organizations break down data silos. In many companies, data is scattered across different departments, systems, and formats, making it challenging to access and leverage effectively. By unifying data, organizations can overcome these silos, enabling better collaboration, data sharing and alignment across the business.
Industries That Benefit Most from Data Unification
From retail to healthcare and financial services to manufacturing, organizations of all shapes and sizes rely on data to drive decision-making, enhance customer experiences and fuel innovation.
However, the sheer volume and complexity of data present significant challenges for businesses seeking to harness their full potential.
Data unification can serve as the linchpin for achieving a unified view of customers, products, operations and more, empowering organizations to extract actionable insights and drive sustainable growth.
Let’s delve into the industries where data unification plays a pivotal role in unlocking value and driving competitive advantage.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers operate in a complex ecosystem characterized by global supply chains, advanced technologies, and ever-changing customer demands.
Data unification enables manufacturers to integrate data from sensors, IoT devices, production systems and more resilient supply chain networks.
This unified data approach facilitates predictive maintenance, improves product quality, and enhances supply chain visibility, driving operational efficiency and agility.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital transformation, with vast amounts of data generated from electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, wearable devices and more.
Data unification enables healthcare organizations to consolidate and harmonize this disparate data, providing clinicians with a comprehensive view of patient history, treatments and outcomes.
This unified data approach enhances clinical decision-making, enables population health management and improves patient care coordination through the development of comprehensive provider hubs.
Financial Services
In the highly regulated world of financial services, data accuracy and integrity are non-negotiable.
Data unification enables banks, insurance companies and investment firms to integrate data from disparate sources such as core banking systems, CRM platforms and transactional databases.
This unified data approach enhances risk management, enables personalized customer experiences and improves regulatory compliance efforts.
Retail and E-commerce
In the fast-paced world of retail and e-commerce, using customer data to understand preferences and predict trends are paramount for success.
Data unification enables retailers to seamlessly integrate data from online transactions, in-store purchases, social media interactions and loyalty programs. By creating a unified view of customer behavior and preferences, retailers can personalize marketing efforts, improve product recommendations and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Energy and Utilities
Energy and utility companies manage vast infrastructures and diverse datasets related to energy production, distribution and consumption. Data unification enables these organizations to integrate data from smart meters, SCADA systems, weather forecasts and billing systems for customer data.
This unified data approach facilitates predictive maintenance, enables energy usage analytics and supports sustainable energy initiatives, driving operational excellence and environmental stewardship.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications companies are at the forefront of the digital revolution, providing connectivity and digital services to billions of users worldwide.
Data unification enables telecom providers to merge data from network infrastructure, customer interactions, billing systems, and IoT devices. This unified data approach enhances customer data segmentation, enables targeted marketing campaigns, and improves network performance and reliability.
As industries continue to evolve in the digital age, the importance of data unification will only continue to grow, catalyzing business success and competitive differentiation.
Components of Data Unification
There are a few discrete steps and components to unify data, including:
Data Profiling
The process of data profiling involves analyzing data sources to understand their structure, quality and content. This involves identifying anomalies, inconsistencies and data quality issues that need to be addressed.
In data profiling, the frequency and distribution of data values are measured on relevant structural levels. Data profiling can also be used to discover the keys that relate to data entities across different databases and to the degree that this is not already done within the single databases.
Data profiling can directly measure data integrity and be used as input to set up the measurement of other data quality dimensions.
Data Cleansing
Data cleansing involves correcting errors, inconsistencies and duplicates in the data to ensure its accuracy and reliability. This may involve processes such as data validation, deduplication and enrichment.
Often, commercial tools can help correct or remove errors and inconsistencies within the data. They can automatically standardize formats, eliminate duplicate records and address missing or inaccurate data values, improving data accuracy and completeness.
Data Integration
Data integration involves bringing together data from different sources into a unified dataset. This involves mapping data fields, resolving conflicts and ensuring compatibility between data sources before they are joined or appended within a database of synchronized data.
Both purpose-built extract, transform and load (ETL) systems and data quality management (DQM) tools exist for integration workloads. Commercial, cloud-native MDM platforms can also be considered comprehensive data unification platforms that also include enterprise integration functionality for building a comprehensive master data model to power downstream analytics from synchronized data.
Data Standardization
Data standardization includes normalizing data formats, structures and values to ensure consistency across the unified dataset. This may include standardizing naming conventions, units of measurement and data formats.
By standardizing data, organizations can improve data quality, accuracy and reliability, laying a trusted foundation for effective decision-making and operational efficiency.
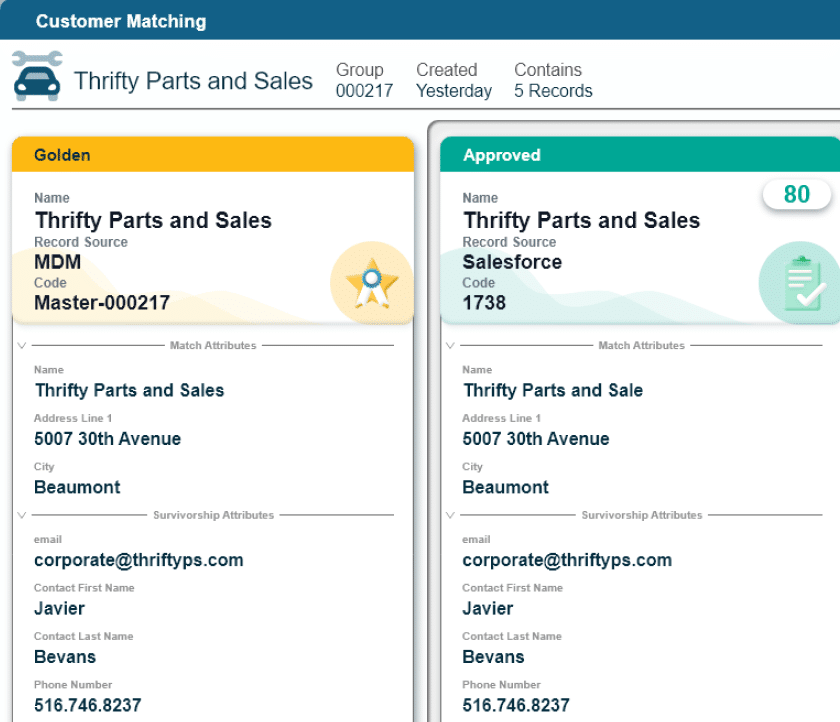
Data Matching and Merging
Matching, merging and survivorship is the process of identifying and resolving duplicates or conflicting records to create a golden record or master data entity. Customer data unification often also includes the process of identity resolution to accurately determine whether multiple records with similar data are, in fact, a single person.
This involves comparing data records, establishing matching criteria (often using fuzzy matching) and merging or consolidating duplicate records. Data synchronization between systems is also often achieved in an operational implementation style.
Data Governance
Data governance involves establishing policies, processes and controls to manage and maintain the unified dataset effectively — with the end goal of ensuring high quality through the complete lifecycle of your data.
This includes defining data ownership, access rights and data quality standards, as well as implementing mechanisms for data lineage, auditability and compliance.
Data Unification Best Practices
Data unification is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution and ongoing management. To ensure successful outcomes, organizations must adhere to best practices that optimize efficiency, accuracy and reliability.
Here are some essential best practices for data unification:
- Define clear data unification objectives and priorities based on business requirements and strategic goals
- Invest in MDM tools and processes to ensure the accuracy, completeness and consistency of the unified dataset
- Implement data governance mechanisms to establish accountability, transparency and control over the unified dataset
- Foster collaboration between IT and business stakeholders to ensure alignment and maximize the value of unified data for decision-making and operational excellence
- Regularly monitor and measure the effectiveness of efforts to unify data to identify areas for improvement and optimization
Difficulties in Data Unification
While data unification offers numerous benefits, it also presents various challenges that organizations must overcome. From data quality issues to compatibility concerns, navigating these difficulties requires strategic planning, robust tools, and effective processes.
In this section, we’ll explore the common challenges and difficulties that organizations encounter when trying to unify data, offering insights into how organizations can address them to achieve successful outcomes.
Data Quality Issues
Incomplete, inaccurate or inconsistent data can pose challenges to teams as they work to unify data, requiring extensive cleansing and validation efforts. Without a commercial platform to automate this process, data stewards may need to manually reconcile data in Excel or other applications.
Compatibility Challenges
Integrating data from disparate sources with different formats, structures, and schemas can be complex and time-consuming, requiring robust data integration and transformation capabilities. Again, commercial MDM or ETL tools can automate and streamline this process and incorporate it into ongoing data workloads.
Scalability Concerns
Managing large volumes of data and increasing data demands requires scalable solutions and infrastructure to ensure performance, reliability and agility.
Profisee MDM: Empowering Companies with Data Unification
Profisee MDM is a comprehensive data unification platform, providing organizations with the tools and capabilities they need to achieve seamless integration, cleansing and harmonization of data.
With advanced data profiling, matching and mastering functionalities, Profisee MDM ensures the accuracy, consistency and reliability of master data entities, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and drive operational excellence.
By leveraging Profisee MDM, organizations can:
- Streamline the data unification process with automated workflows, rules-based matching algorithms and configurable data quality rules.
- Improve data quality and governance with built-in data cleansing, validation and enrichment functionalities, as well as data lineage and auditability features.
- Gain actionable insights into data relationships, dependencies and usage patterns to optimize data unification efforts and maximize the value of unified data.
- Scale effortlessly to manage growing data volumes and complexities while maintaining performance, reliability and compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Interested in learning more about the potential of adaptive MDM? Explore the Profisee Platform or schedule a custom demo today to learn how you can streamline data standardization initiatives, ensuring consistent, reliable data across the enterprise.

Benjamin Bourgeois
Ben Bourgeois is the Head of Product and Customer Marketing at Profisee, where he leads the strategy for market positioning, messaging and go-to-market execution. He oversees a team of senior product marketing leaders responsible for competitive intelligence, analyst relations, sales enablement and product launches. He has experience managing teams across the B2B SaaS, healthcare, global energy and manufacturing industries.