- Key Characteristics of Golden Record Data
- Why Do You Need to Have a Golden Customer Record?
- Golden Record Architecture and Lifecycle
- How to Create a Golden Record in MDM
- Use Cases of Golden Records in Master Data Management
- Common Challenges in Golden Record Management Systems
- Create and Manage Your Golden Record with Profisee
- Frequently Asked Questions About Golden Records
Key Takeaways
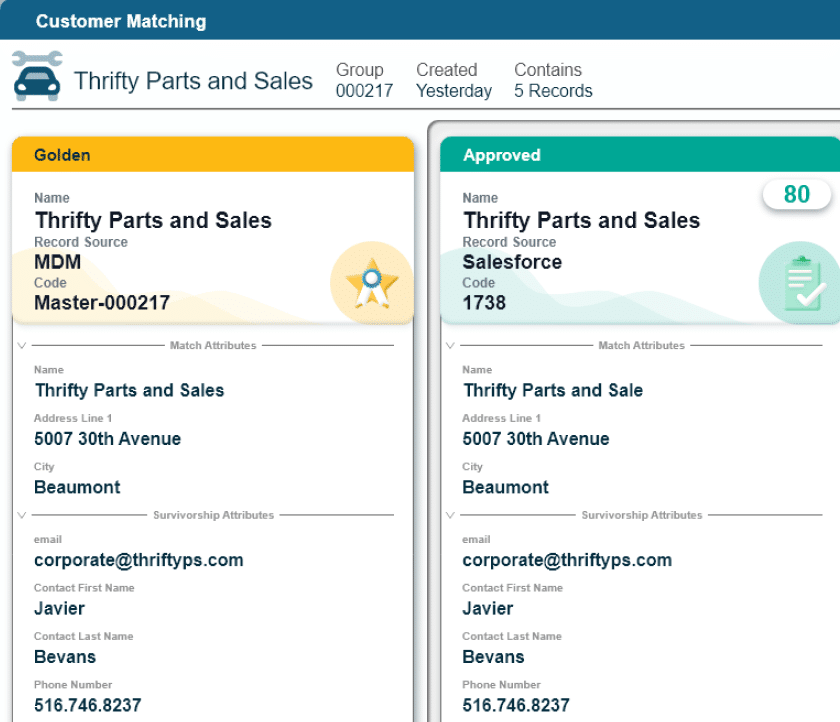
A golden record in MDM is a complete and accurate version of a data point stored where it can be accessed by the entire business.
Golden records help solve many business challenges, like conflicting data, siloed systems and customer fragmentation.
There are six steps for creating a golden record: data ingestion, data matching, survivorship rules, validation, publication and maintenance.
A robust MDM platform like Profisee facilitates the move from raw data from sources to the trusted golden record that can be used by the entire organization.
A golden record in MDM is a complete and accurate version of a data point stored in a master data management solution where it can be accessed by all connected business systems. A golden record achieves the highest quality standards as it is unique, correct and verified.
For example, a contact golden record would contain verified and correct information for a business contact’s name, email address, company, job title, physical address and phone number. All other variations of the same person from data sources across the company would be replaced with the golden record.
The term golden record is also used to reference the totality of verified entries within a domain or all verified domains within the business data set. For the purposes of this article, we will use the term golden record to refer to the single piece of verified data rather than the sets.
The State of Master Data Management (MDM) 2026
Key Characteristics of Golden Record Data
A golden record can be classified as such because it is the most reliable, high-quality record available. The meaning of a golden record does not require that the data is stagnant, but that it is easily updated and continuously verified as high-quality by business teams and third-party sources.
Because quality is difficult to quantify, a golden record is identified by a few key characteristics, including:
- Accuracy: Golden data is verified for correctness and documented where it’s accessible to all.
- Completeness: The record of data has as much information as is available. So, while not all contacts will have an office phone and cell number, a golden record would have at least one.
- Uniqueness: Within the entire business’s golden dataset, each individual record should be unique with no duplicates or near-duplicates.
- Timeliness: The record is updated as soon as new or changed data is shared and verified.
- Trustworthiness: The golden records are considered the single source of truth and consistently used by the business.
Why Do You Need to Have a Golden Customer Record?
Each business unit that touches any record will help build the consensus that forms a golden record by adding data. While the CRM may include a vendor’s home office address and sales contacts, the manufacturing arm may include warehouse addresses and contacts.
You need a golden customer record because each of these bits of information taken separately are raw data sources that don’t provide the full picture of a vendor. When all information about a vendor (or customer, or product) is together in the golden record, business units can make faster decisions and engage in cross-team collaboration that speeds business operations.
Eliminate Duplicate or Conflicting Data
Duplicate and conflicting customer data confuses employees and can cause revenue-impacting delays or even regulatory issues. Incorrect or repeated data may also cause confusion when attempting to train GenAI models. A prediction from analyst firm Gartner says that 30% of GenAI projects will be abandoned by the end of 2025 due to poor data quality, which includes inaccurate data and other concerns.
Why a golden record works: The golden record eliminates duplicates by default and brings conflicting customer records to light so teams can verify the right data. As a result, business users can confidently reach out to the right contact, send information to the right email addresses and break through to the decision-makers when changes are needed.
Consolidate Siloed Systems
An ERP doesn’t necessarily speak with invoicing and financial systems, or integrate with contract management software, often making data transfer a manual process that slows operations and increases the risk of time-consuming errors. Customers feel that speed, with 62% of business leaders surveyed in 2023 saying bad data slowed their business operations.
Why a golden record works: A software that was previously siloed can access the right data quickly in a golden record MDM software. This data unification improves the customer experience, as contracts don’t need revisions due to typos, for example, or customer hand-offs from different parts of the organization happen seamlessly.
Reduce Customer Fragmentation
Because the team stores data in many different systems that don’t necessarily speak to one another, bits and pieces of customer data may exist in different systems. This makes it challenging to produce a full picture of the customer to understand their preferences, needs and even current or past deals.
And customers notice. A 2023 Salesforce survey found that 65% of customers expect companies to “adapt to their changing needs and preferences,” but 61% of customers feel like nothing more than a number.
Why a golden record works: Golden record master data centralizes all customer information, creating a customer 360 record, giving everyone a full picture of the extent of the data that exists for the customer. This data unity can improve analytics, better customer relationships and speed deals.
Increase Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory requirements carry with them the added burden of deadline-based action. Whether the team must fulfill a data request or produce customer records for audit, timeliness and accuracy count in the face of federal or regional regulations.
Why a golden record works: Golden record data improves regulatory compliance as the team does not have to search through several siloed systems to fulfill a GDPR data deletion request, and customer records can be clearly audited for financial compliance purposes, such as KYC and AML compliance.
Golden Record Architecture and Lifecycle
Producing and maintaining MDM golden records require a broader governance and process architecture that supports and sustains up-to-date records across data domains and throughout the organization.
To do this, the organization can build processes around a medallion architecture for MDM.
Medallion Model: Bronze, Silver, Gold Layers
Within the medallion model, just like Olympic medals, there are bronze, silver and gold data layers.
- Bronze: Raw data that lives in or is pulled from source software.
- Silver: Processed and mapped data stored in a central location.
- Gold: Mastered golden records stored in MDM.
By classifying data with the medallion model, the team has a common language they can use to reference data’s readiness for use across the organization.
How to Create a Golden Record in MDM
A golden record MDM project takes planning and coordination across many departmental stakeholders in the organization. These steps outline necessary items to plan for.
Step 1: Ingest Data from Multiple Sources
The process of building a golden record starts with gathering data. Try to get the most complete data from as many sources in the organization as possible. Key internal systems include:
- CRM
- ERP
- Marketing automation
- Accounting
- Contract management
- Inventory
Consider departmental data silos, like:
- Finance
- Marketing
- Manufacturing
You may also want to consider external and third-party data sources, such as:
- Map applications
- Public records
- Data enrichment applications
The process of data ingestion should also include data normalization and preparation. At this point, you should consider the formats that data will take and what transformations need to be done to achieve those formats. Preparing the data as you pull it from sources will ready it for step 2. A robust master data management solution like Profisee will allow the data teams to program data formats and transformations for faster data ingestion.
Single Source vs. Multiple Sources for the Golden Record
While it may be tempting to start a golden record initiative from a single source, that approach may present challenges down the road that are best dealt with by planning to integrate multiple sources from the start.
| Single Source | Multiple Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Challenges |
|
|
Step 2: Match Records That Refer to the Same Entity in Golden Record Master Data
Data matching without automation is time-consuming and tedious, but today’s MDM systems use matching techniques like rule-based, probabilistic and fuzzy matching to identify matches and near-matches across your data.
These techniques all match data sets, but with varying levels of precision or sophistication. Profisee fuzzy matching logic identifies and groups potential duplicates and incomplete records for data standardization without highly-manual processes.
| Data Matching Technique | Precision | Error Rate | Method | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-based matching | High | High | Matching rules are set by the data team. | Match highly structured data with consistent formats |
| Probabilistic matching | Medium | Medium | Match data based on probability of correctness for sets. | Less structured data with unique or near-unique characteristics like social security numbers, unique user ID |
| Fuzzy matching | Low | Low | Matching based on sets of characters, number of edits or phonetics/sounds | Messy data from several systems with a likelihood of typos or other errors. |
Step 3: Apply Survivorship Rules to Determine the Best Values
Survivorship rules set by the organization according to MDM best practices will help you understand which data should be prioritized within the system when there are conflicting entries. Depending on the systems you use or the team’s understanding of organizational processes, the priority of data, also known as survivorship logic, may change.
For example, a company may prioritize the most recent data entry as correct, known as a recency rule, or the data entered in the inventory software rather than the CRM, which is a system prioritization rule. Some other survivorship rules to consider include:
- Minimum or maximum value signals priority
- Aggregated data from all systems is included
- Most complete data is considered priority
- Custom rules based on organizational needs
When building data survivorship rules, try to define based on long-term needs, not on immediate data matching. These rules will help determine future data governance patterns.
Step 4: Validate and Enrich the Golden Record Data for Accuracy and Completeness
Quality, usability and completeness of the golden record are improved and maintained through enrichment and validation. Data undergoes enrichment when it receives new information from internal or external sources, filling in blanks where the data is missing.
For example, the customer email may exist alongside the name in the CRM, but the business locations and company name live in the ERP. Enrichment in MDM platforms like Profisee brings these records together in a single, golden record.
Validation confirms or denies the data is correct through comparison with other sources. In the case of customer data, you might use LinkedIn to validate names, job titles and company names, or publicly available location data to verify an office address.
Some validation rules to consider:
- Designate required vs. optional fields within the data set: You may not require a job title for all customers, or a second address line.
- Set specific formatting rules: You may require a full first name rather than an initial, or divide first and last names into separate columns. These rules can also extend to how email addresses or phone numbers appear.
- Referential checks: These checks make sure that the information is in the right hierarchy (parent/child) or exists in the correct relation, for example, a vendor company and their location.
Validation and enrichment work together to make the golden record the most complete and correct record.
Step 5: Publish the Golden Record to Downstream Systems
The most exciting part of the process is pushing golden records to the business systems across the company. This still takes some planning, as you want to make the process as consistent and timely as possible.
Many organizations use data lakes to store golden records for access by a variety of downstream systems. Tools like ERPs, business intelligence (BI) software and CRM software can access golden record data as needed from the data lake via API connections, ETL, or even CSV uploads.
While you can transfer golden record data to software in several ways, APIs build a continuous connection to business systems that removes manual labor. As you build these connections, identify what data needs to move to the downstream endpoint, like the CRM or ERP and leave out the unnecessary data.
While real-time data updates may not be required for every organization, timing when you publish golden record updates correctly will help the team see the value of the golden record master data management project.
Step 6: Maintain Ongoing Data Governance and Stewardship
Maintenance of golden records requires continuous monitoring and governance, as typos, incomplete forms and other everyday mishaps can tarnish the data’s reliability. Building automated governance rules within a data stewardship solution that reinforces your cleansing, validation and survivorship rules will do much of the work.
But computers can’t do analysis and inference that’s sometimes needed for reliable data. Human-in-the-loop approval workflows that flag potential mismatches for validation can help optimize the quality of automated rules. Profisee combines notifications of potential errors with audit trails and change logs to help the team track and analyze data. The team can then consider rule edits for edge cases based on behavior, improving the overall quality of the data.
Change management within the team is crucial to ensuring data is completed correctly the first time. Coach business users on the importance of sticking to requested formats and give examples of how consistently reliable data improves their work environment.
Use Cases of Golden Records in Master Data Management
Golden records not only support businesses in their need for efficiency and reliable data. They also improve customer experiences because organizations become better informed, more agile and provide a more personalized experience.
| Golden Record Use Case | Business Outcome | Customer Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Complete customer profile | Customer 360-degree view | Purchase and experience history taken into account within interactions, personalized ads or marketing |
| Centralized records, audit logs | Regulatory compliance | Trust in the brand, ability to remove personal data quickly |
| Supplier data | Supply chain data optimization | Faster delivery, higher quality products, lower prices |
| Medical records | Patient records management | Unified experience across practices, increased safety |
Common Challenges in Golden Record Management Systems
Any technology initiative comes with challenges. Golden record management projects affect the entire organization and touch every business system that uses those records. You can overcome these challenges with careful planning.
Source System Inconsistencies
Because organizations use many systems across different departments, these systems will have a multitude of data formats and will likely need to pay careful attention to data deduplication, matching, validation and enrichment.
Best practice: Start the golden record process with a single data domain that is useful to all business teams. This will expose many of the inconsistencies from the beginning, allowing the data team to fully understand them. And because the domain affects people across the organization, the value of the completed golden record will become clear early in the process.
Change Management Resistance
People don’t like to change their processes, even if the change will save them time, work or headaches. You will receive resistance to any new system, but by planning and communicating with teams, you can get everyone working the same systems quickly.
Best practice: Include teams in your initial understanding of the data quality problems and have them help you expose inconsistencies or workarounds they use in their processes. This will show that you care about their problems and want to help. Consistent communication on a schedule will also help the team know when they’ll participate in training and implement the new systems.
Ongoing Validation Complexity
Validation and data reliability need constant attention to keep up with the flow of information into and through the organization. Many organizations find this challenging. Some may feel their work is done once golden records are established and pushed downstream. But consistent validation will actually lighten the load, so the team doesn’t have to repeat the golden record process from scratch.
Best practice: Establish mapping, cleansing, deduplication and validation rules early and then use a data governance platform to enforce those rules. Automating this process as much as possible will reduce the workload on the data team, especially if they can manage data by exceptions to the rules.
Data Privacy Concerns
Any discussion about data will bring up data privacy concerns. Customers, vendors and partners want to know that their data is safe and secure. They don’t want it stored all over the organization, and they want to be able to delete or update it as necessary.
Best practice: Golden record management actually makes data more secure, as systems rely on the golden record instead of siloed data across the organization. That said, the latest cybersecurity and data security procedures should be followed to protect the golden records in transit, at rest and within downstream systems
Create and Manage Your Golden Record with Profisee
Golden record creation and management require planning and work. Profisee’s golden record management solution makes it easy to level up your golden record data with time-saving workflows, AI-powered fuzzy matching technology and a flexible integration approach that works with your existing systems.
If you’re ready to move from bronze to gold, request a demo.
Frequently Asked Questions About Golden Records
How Do I Maintain the Accuracy of a Golden Record?
Golden record maintenance requires the company to adhere to data governance frameworks, survivorship and validation rules as set up within a data governance or MDM program. Enforcing these rules across the organization will contribute to continued accuracy and periodic evaluation and validation of golden records will check for accuracy.
How Can I Use Data Analytics for Golden Record Management?
Data analytics will help the organization set metrics of quality and analyze the quality of data from sources as well as the golden records. Data analytics can help the team find patterns in the cleansing and matching stages that may signal an operations change in a department, or they can identify when governance rules may need revision.
What Is the Future of Golden Customer Record Management?
Golden customer record management is evolving from a static master file that sits in the database — waiting for updates or use — into a real-time customer intelligence asset. This enhanced customer view can provide the sales and marketing teams with personalization insights that improve sales and cut down sales cycles.
The increased speed of data movement across the organization requires management and analysis tools that can keep up with that pace. Companies that invest in robust business intelligence and analytics software will use golden record customer intelligence to predict market movements and stay ahead of trends.
All these changes mean governance and stewardship have to keep up to maintain high-quality data. Companies must implement workflow automations and artificial intelligence to continue to build usable golden records, rather than drown under the deluge of organizational data production.

Tamara Scott
Tamara Scott is a writer, editor and content strategist with over a decade of experience located in Nashville, TN. Tamara holds a Master's in English from Belmont University, formerly served as Director of Content for TechRepublic, and her work has appeared in ServerWatch and EPI-USE.com, among others. When she's not crafting SEO-informed and conversion-ready content for SaaS and IT service companies, she's probably at home on her pottery wheel. Connect with her on LinkedIn.