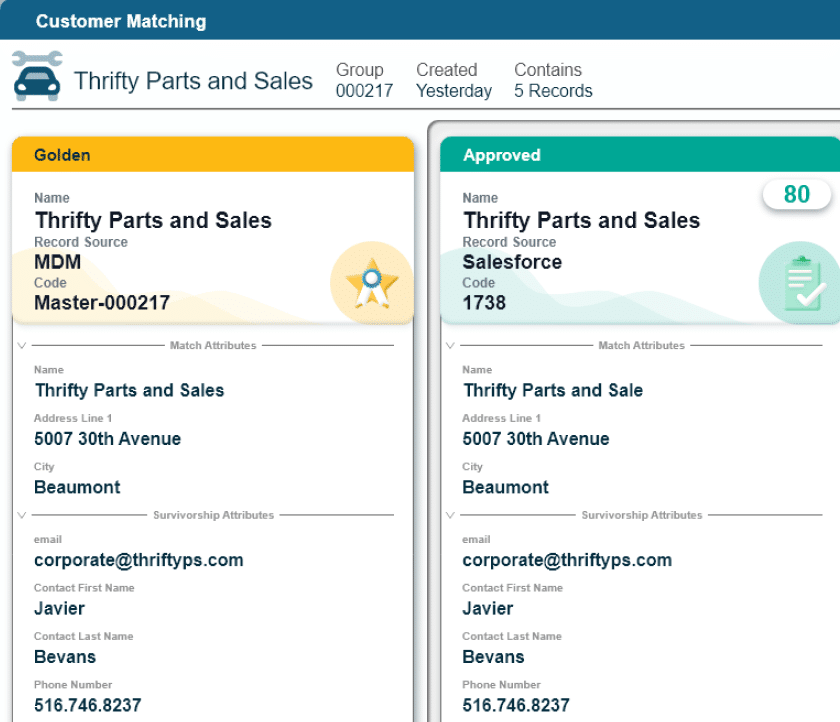
Key Takeaways
PMDM creates a single, trusted source of product data by integrating, cleansing and standardizing product information across systems, enabling better decision making and operational efficiency.
It supports critical business functions across buy-side, inside and sell-side processes, improving customer experiences, ensuring regulatory compliance and reducing costs.
Successful PMDM implementation requires overcoming challenges such as data integration complexity, change management and ongoing maintenance, but the benefits can significantly impact business growth and performance.
Effective data management is crucial for businesses looking to stay competitive. One critical component of enterprise data management is product master data management (PMDM), a practice that ensures the integrity and consistency of product data across an organization. In this article, we’ll explore what PMDM is, why product data is important, the advantages of PMDM and some common challenges organizations face when implementing it.
The State of Master Data Management (MDM) 2026
What Is Product Master Data Management (PMDM)?
Product master data management (PMDM) refers to the process of managing and maintaining a single, cohesive view of all product-related data within an organization (also known as product 360). This includes product descriptions, dimensions, pricing and other product attributes essential for business operations. PMDM ensures that product data is accurate, up-to-date, trustworthy, accessible and standardized across various departments and systems, helping leaders make better decisions and improving operational efficiency.
Gartner defines three different use-case scenarios for product master data management: buy side, inside and sell-side.
Buy-Side Use Case for PMDM
Buy-side refers to the products and materials purchased from suppliers. In this scenario, the product data and attributes typically originate outside of your organization.
However, the attribution may not be sufficient to support the systems and processes that will depend upon the buy-side products. In this use case, MDM is often used to validate, enhance or enrich product data with corrected attributes, additional attributes and various product classifications.
Inside Use Case for PMDM
The inside use case refers to managing product data as it moves from system to system and process to process within your organization. In this use case, the product data could be about products and materials acquired from suppliers or finished goods or both.
For an inside use case, product data may require additional validation or enhancement as it moves from system to system. Additionally, each system or process may contribute additional product attribution or classification information that needs to be shared with other systems and processes. MDM supports both of these scenarios.
Sell-Side Use Case for PMDM
The sell-side use case refers to making product data about finished goods ready for go-to-market. For retail and consumer packaged goods (CPG) organizations, this means ensuring product data is ready for omnichannel, which typically entails adding and managing sales-oriented descriptions — often in multiple languages — as well as images and videos of various resolutions. The highly specific sell-side use case is often supported by specialized product information management (PIM) tools, whereas B2B sell-side, buy-side and inside PMDM use cases are achieved by using an MDM tool like Profisee.
Data organizations typically handle product data management, using an MDM tool to integrate product data from various source systems, cleanse the data and standardize it according to the organization’s data governance policies. In this way, organizations can create a single source of truth for trusted data about their products for a variety of benefits beyond just improved data quality.
Why Product Data Is Important
Product data plays a pivotal role in numerous business functions, from supply chain management to sales and marketing.
Consistency Across Systems & Channels
According to a McKinsey B2B Pulse Survey, the number of sales channels that customers interacted with increased from five to 10 or more between 2016 and 2021. Given this trend towards omnichannel sales, it’s becoming more and more important to give customers consistent experiences
Having high-quality product data is critical for building seamless multichannel sales experiences. That means whether a customer is shopping online, in your app or in one of your stores, they will see the same accurate information about a product, like pricing and availability.
Enhanced Customer Experience
With data becoming more prolific and widespread every year, your customers gather information about your products and services through a variety of sources and from different teams and functions within your organization. If a product’s specifications listed online do not match those in marketing materials and do not match the specifications shared by the sales engineer, a myriad of problems can ensue.
Customers may acquire the incorrect or inapplicable product, you may have to deal with costly return and rush re-shipment scenarios, your organization may have to embark on costly research and remediation to identify and correct discrepancies, and ultimately, your customer may lose trust in your brand and your products.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have strict regulations regarding product information, making accurate product data management crucial. A mistake or inconsistency in a medication’s dosage labeling, for example, could lead to sub-optimal health outcomes at best or harm someone at worst — not to mention accompanying liabilities in the form of recalls, fines or lawsuits.
Operational Efficiency
Inconsistent data and uneven access to data across departments keep your organization from operating at peak efficiency. Inconsistent data causes errors that someone must spend time or company resources fixing, and data stuck in silos across departments creates bottlenecks that slow down operations.
Good product master data management alleviates these pain points, giving everyone access to a single, trusted repository of data, opening access to data for use across the enterprise and helping to automate previously time-consuming and tedious processes.
Better Decision-making
With accurate, up-to-date, trustworthy product data, organizations can derive better insights from analytics, leading to better decision making. This is especially true in the age of AI, when tools like AI copilots require a foundation of accurate, trustworthy data to produce reliable insights. This will only become more important as more stakeholders across the enterprise start incorporating AI tools into their daily workflows.
Advantages and Challenges of Product Master Data Management (PMDM)
Implementing PMDM comes with a host of benefits that can significantly impact an organization’s efficiency and bottom line. However, PMDM also presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure successful implementation.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Improved Data Quality: Tools for managing product master data provide tools for data validation and cleansing, promoting high data quality | Data Integration: Integrating data from various sources can be complex and time-consuming, especially when using tools that only support pre-built integrations |
| Centralizing Data Governance: PMDM helps create a single source of truth for product data, minimizing discrepancies and promoting consistency | Data Entry Issues: Incomplete or inconsistent data entry can hinder the effectiveness of PMDM systems |
| Cost Reduction: PMDM reduces costs associated with data errors, rework and inefficient processes | Change Management: Implementing PMDM can require significant changes in processes and culture, which can face resistance |
| Better Decision-making: With clean, unified data, organizations can make more informed, data-driven decisions | Technology Costs: The initial investment in PMDM technology can be substantial, particularly for smaller organizations |
| Scalability: PMDM facilitates seamless data management across various departments and locations, supporting business growth | Ongoing Maintenance: Continuous oversight is needed to keep data accurate and systems up to date, requiring dedicated resources and expertise |
| Avoiding Supply Chain Disruptions: Maintaining up-to-date inventory counts and being able to accurately forecast demand for different products is key to avoiding supply chain disruptions |
Manage Your Product Master Data with Profisee
Profisee is a multidomain master data management (MDM) tool that lets you easily manage product data from any source. We take an adaptive approach to MDM, meaning our platform adapts to the processes and technology you already use — not the other way around.
Use Profisee to integrate your product data from your source systems and use the platform’s ML-powered features to match, merge, de-duplicate and standardize records to create a single source of truth for accurate, uniform and trustworthy product data. When you’re done, it’s easy to make data available to the systems that need it, be it business intelligence (BI), marketing automation or AI tools.
Schedule a demo today to see for yourself how Profisee can help your organization make the most of its product master data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Product Master Data Management Process?
The product master data management (PMDM) process encompasses a series of structured steps designed to ensure the efficient management of critical product information throughout its lifecycle.
- The process begins with data sourcing, where information is collected from various internal and external sources, including suppliers and market data.
- The data integration phase consolidates disparate datasets into a comprehensive repository, eliminating data silos.
- Data stewards match, merge and de-duplicate data to combine similar records before standardizing records in accordance with your organization’s data governance policies.
- Finally, the newly created golden records are made available to the downstream systems that need access to it, like business intelligence (BI) or AI tools.
Overall, the PMDM process facilitates informed decision-making and strategic planning by providing a reliable foundation of product data across the organization.
What Is the Difference Between Product MDM and PIM?
Product master data management (MDM) and product information management (PIM) serve distinct yet complementary roles in the realm of product data management.
Product MDM focuses on the authoritative governance and integrity of master data across the entire organization. Its primary objective is to ensure a single, accurate version of product data that can be used for analytics, compliance and strategic decision-making.
By contrast, PIM is primarily concerned with the creation, management, and distribution of rich, often nonstructured product information, such as descriptions, images and specifications, which is essential for marketing and sales. While MDM provides a foundation for data accuracy and consistency, PIM enhances this data with detailed content that caters to the specific needs of various sales channels.
MDM establishes the “who” and “what” of products by maintaining a trusted source of truth, whereas PIM addresses the “how” by delivering product information in a way that optimizes customer engagement and drives sales performance.
How Does Product MDM Differ from Customer or Other MDM Domains?
When we talk about data domains in the context of master data management, we’re referring to the high-level blocks of master data that help data professionals logically group or organize data. Product master data is, of course, one domain, but other common domains include customer, vendor, supplier and location data.
These “big blocks” all represent master data, but not all master data can or should be managed the same way. Compared to, say, customer data, product data can be more complex and varied since it inherently focuses more on physical attributes, classifications and regulatory compliance. Product data is also used for different use cases — such as supply chain management — and has different governance needs.
Taking a multidomain approach to master data management is generally a good idea, and that’s especially true for product data. Because product data touches so many other parts of a business (customers, suppliers, locations), having a holistic view of your product data will be much more beneficial in terms of business outcomes than managing it by itself.
Why Is Multidomain MDM Important?
As mentioned above, there are different types of master data domains organizations might manage depending on their MDM strategy. It’s easy to imagine these data domains existing separately in neat groupings, but in reality, master data is threaded together across domains in a web of complex interactions and relationships.
For this reason, it’s important to take a multidomain approach to MDM. But this wasn’t always easy to do. Legacy MDM platforms usually only focused on one type of domain. For example, organizations would have to buy separate solutions to master their product and customer data, making it cumbersome and costly to get more unified views of data.
Multidomain MDM solutions like Profisee make it easier — and much more affordable — to create holistic views across data domains. This simplifies things from a technical perspective, but it also makes it easier and faster to generate cross-domain insights that lead to improved decision-making. Businesses can also get more creative with MDM use cases with multidomain MDM, enabling initiatives like more seamless customer experiences, better supply chain management and better contracts with suppliers.

Forrest Brown
Forrest Brown is the Content Marketing Manager at Profisee and has been writing about B2B tech for eight years, spanning software categories like project management, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and now master data management (MDM). When he's not at work, Forrest enjoys playing music, writing and exploring the Atlanta food scene.