Key Takeaways
Departments across the organization use data from a vendor master file.
Security and role-based access to the file can have regulatory and compliance implications.
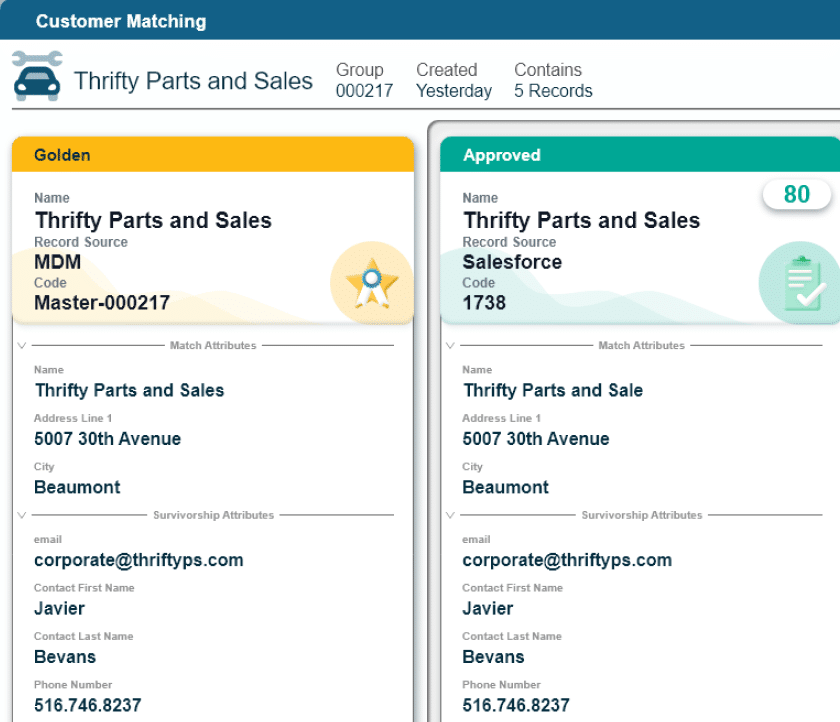
Automated MDM software helps companies manage vendor master files by exception rather than manual verification.
The security and accuracy of your vendor data directly affect the relationships you have with them and the deals you make with them. Vendor data includes contact names, banking information and tax identification numbers — sensitive information that must be secured for regulatory compliance.
Keeping a vendor master file up to date with accurate and reliable information affects every part of the business, from accounts payable to sales and human resources. These best practices will help your business establish and maintain a usable vendor master file.

Accelerate Microsoft Fabric Success
What is a vendor master file?
A vendor master file stores the most recent, complete and accurate information about vendors. A vendor could be anyone you pay, from suppliers to contractors, and will often contain highly sensitive information including bank account numbers and tax identification numbers (EIN or SSN) in addition to contact names, phone numbers and addresses.
Departments across the organization will use the vendor master file to
- Find contact information for a current vendor
- Make requests to pay vendors/submit invoices
- Pay vendors
- Update vendor information
Because of the broad use of the file and its potentially sensitive information, companies need to pay particular attention to the accuracy and security of a vendor master file. A master data management (MDM) tool can speed up this otherwise highly detailed manual process.
How to Clean Your Vendor Master File
To get to the most accurate version of a vendor master file, the data in that file must be analyzed and cleansed. Look for entries that duplicate or contain duplicate information as other entries, inactive vendors and missing information.
Duplicates
Duplicate entries often happen because of spelling, capitalization or formatting mistakes in one or more fields within an existing or new entry. This is especially problematic for vendor master files because errors within banking or tax information could result in missed payments or incorrect filings. Internally, duplicates could throw off financial reconciliation or payment audits.
Clean potential duplicates from the file by flagging and analyzing any duplicate or similar fields within properties including addresses, phone numbers, bank account numbers and last names. First name fields may produce too many false positives, so consider leaving that property out of your search. If you spot a duplicate or near-duplicate, consider whether you should:
- Combine vendors that were entered more than once
- Maintain vendors that appear as duplicates but come from separately billed departments — and ideally — document the hierarchical relationship between the vendors
- Correct vendor information
Inactive Vendors
Depending on your sales cycles and company or regulatory data storage requirements, you’ll want to archive inactive vendors to a secure long-term storage location. Identify your time limit and scan entries for their last interaction or payment. If last interaction isn’t currently a property updated in the vendor file, consider adding that to your vendor master file.
Missing Information
Clean up any empty fields within the vendor data file by scanning the file for empty fields and adding the necessary information. This step may take a bit longer, as you may need to reach out to the vendor directly with this information.
Cleaning the vendor master file can be time consuming, but employing MDM tools can significantly speed the process by scanning the record, flagging items for review and even performing address verification and enrichment through integration with a third-party service like Melissa Personator.
Vendor Master File Management Best Practices
Once you’ve cleaned the vendor data file, all you need to do is maintain it, right? That’s often difficult in practice because so many departments interact with the data in this file. These best practices will help your team maintain an accurate and more usable version of your vendor master file.
Choose (and Enforce) Property Formats
So many master file mistakes result from varied capitalization, spacing, spelling and even content order. Choose what format each field should have and make that consistent across the organization. Some (and certainly not all) formats to pay attention to:
- Capitalization of first/last names
- Hyphens, parentheses, commas and brackets within numeric fields like phone numbers, EIN/SSN and bank account numbers
- Number/word order of addresses
Enforcing formatting within software systems that feed to the vendor file can help maintain these files, but consistent communication to the team and data transformation tools will also assist you in keeping these files clean.
Implement Data Quality Rules (Including Data Validation)
When available, create data quality rules for data validation allowing users to choose options from a dropdown list rather than manually typing in data. For fields like state, country or vendor type that don’t change often, a drop-down will keep data clean and allow the payables team to work by exception for these fields rather than having to continually correct similar errors. Integration with third-party data tools like Melissa Personator or Google Maps Address Validation can help ensure addresses match what the postal service has on file to reduce the risk of misdeliveries.
Set User Permissions to Limits Who Approves Vendor Updates
Can anyone in the company edit vendor data? They shouldn’t be able to. Restrict update access to a small number of need-based administrators or set up review and approval processes that allow the vendor master file to update only when conditions are met.
Provide Onboarding Vendors with a Form or Self-Service Portal
A self-service form or portal that asks vendors to enter their own information in the manner required by the vendor file format may not inherently reduce the number of inaccurate or missing fields — but many form tools can at least enforce simple formatting requirements. Make necessary fields required by the form and double-check any entered information against W9 or other required documents.
Protect Sensitive Information
Decide which roles at the organization should have view, edit or administration to each property within the vendor master data file. The marketing team may be able to view a vendor’s contact name and address but probably will not need access to that vendor’s bank account and EIN. The accounts payable administrative lead may need access to the full vendor data, but other executives and leaders should probably have restricted views as well.
Schedule Audits
Even if you think you’ll remember to audit the vendor master file, schedule the audits and plan for the internal resources to keep those files updated. Note that data teams will often need to engage their business partners closest to the vendor or supplier relationships to make judgment calls based on institutional knowledge.
After that initial cleansing, if your team follows these best practices, subsequent audits should run smoothly.
Automate Updates
Wherever possible, automate updates to the file, whether it’s through data transformation rules that enforce capitalization rules or naming conventions or automatic approval notifications of outliers. Decide on your formats and requirements, program them into your data governance tools, and let the machines do the rest (and notify you of any anomalies, of course).
How to Use MDM for Vendor Master File Management
A master data management solution improves vendor master file management by automating many of the file management tasks on an organization-wide basis. With these tools, departments requiring vendor data can access reliable, usable vendor details when they need them and keep data securely stored at all times.

Forrest Brown
Forrest Brown is the Content Marketing Manager at Profisee and has been writing about B2B tech for eight years, spanning software categories like project management, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and now master data management (MDM). When he's not at work, Forrest enjoys playing music, writing and exploring the Atlanta food scene.