Table of Contents
- What is Data Interoperability?
- The Advantages of Using Interoperable Data
- Importance of Using Interoperable Data
- Challenges Preventing Data Interoperability
- How to Achieve Data Interoperability
- How to Test If Your Data is Interoperable
- Data Interoperability Best Practices
- How Data Interoperability Impacts Different Industries
- Tap Your Data’s Full Potential with Profisee
For organizations looking to become data-driven, there are many situations in which you may need to exchange or use data across systems or even across different organizations. This is where data interoperability comes into play. For anyone whose job involves widely shared enterprise data, understanding the intricacies of data interoperability is essential for using data as a strategic asset and reaping the benefits it can provide.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about data interoperability at a high level, from defining what it is to its advantages, challenges and best practices. Let’s dive in!
What is Data Interoperability?
Data interoperability refers to the ability of different information systems, devices or organizations to access, exchange, integrate and cooperatively use data in a coordinated manner. At its core, it’s about ensuring data can move smoothly and securely across various platforms while maintaining its integrity and utility, no matter the source system.
Example: Data Interoperability in Healthcare
Imagine a large healthcare organization with multiple departments using different software systems. Interoperability lets the organization share patient records, lab results and treatment plans seamlessly among these systems, enabling healthcare providers to offer better-coordinated care without the hassle of manual data entry or transfers.
Data interoperability also serves as the basis for the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard — a set of rules adopted across the healthcare industry to facilitate the sharing of electronic health records (EHR) among different providers and healthcare organizations. FHIR helps providers give patients the best care possible by making it easier for them to access a patient’s health information while empowering patients to take control of their own health information and share it with the provider of their choice.
Using this standard, EHRs can be securely exchanged in JSON, XML or RDF format through APIs — a massive win for operational efficiency compared to traditional methods of sharing patient health information, like faxing copies of patient charts.
The Advantages of Using Interoperable Data
There are multiple advantages of making data interoperable in an organization:
- Streamlined Operations: Processes that depend on data from multiple systems become more efficient by seamlessly sharing data across systems without transformations or manual downloading or uploading.
- Enhanced Decision-making: Decision-makers gain access to comprehensive datasets, allowing for better-informed choices.
- Cost Efficiency: Reducing manual data handling lowers the risk of errors and cuts down on operational costs from FTEs.
- Improved Compliance: Interoperable systems can ensure data governance and compliance across various jurisdictions, especially in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance.
Importance of Using Interoperable Data
Data interoperability is important for many reasons — helping companies gain and maintain a competitive advantage chief among them, according to a Moody’s Analytics report. Businesses rely on data from a variety of sources to not only conduct business and maintain business continuity, but also to uncover important insights that leaders use to guide decision-making and business strategies. Without secure, reliable access to third-party data or even proprietary data stored in separate locations internally, that becomes very difficult to do.
Importance in Highly Regulated Industries
Interoperability is key to open data success for businesses across the board, but it’s also a requirement for highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
For Healthcare
We talked about the FHIR standard in the healthcare industry earlier, but being able to share patient information alone is not enough when it comes to health records. Electronic health records must also be shared securely, meaning any software used to facilitate data interoperability for healthcare organizations must be HIPAA compliant.
HIPAA compliance sets strict standards for how patients’ health data can be stored, shared and accessed to ensure that unauthorized parties do not gain access to sensitive information. This usually means that systems used for storing and transferring personal health information (PHI) must use encryption both at rest and in transit in addition to the product vendor having employee training programs, physical security measures and incident response plans, among other requirements, in place.
For Finance
Data interoperability is particularly important for financial services businesses, such as banks, credit card companies and insurance companies. While not a compliance standard enforced by any government regulatory body, Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) is a set of standards administered by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council that applies to all organizations that process credit card information.
PCI DSS exists to protect both credit card issuers and customers, defining standards for how companies should store, process and transmit cardholder data. This includes mandating the encryption of cardholder data on public networks, implementing firewalls to block access to unauthorized users and protecting systems against malware.
Data interoperability also plays a key role in helping corporations maintain compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Companies not only rely on data interoperability to keep accurate accounting records, but they also use it to comply with data retention requirements for certain types of financial information.
Challenges Preventing Data Interoperability
Despite its importance, there are multiple factors that can negatively impact an organization’s ability to use data interoperability:
- Legacy Systems: Older systems may not support modern interoperability standards like APIs, causing integration challenges.
- Data Silos: Different departments and teams within the organization use different software systems. This leads to data getting siloed in multiple different systems, making data sharing difficult.
- Inconsistent Standards: Varying formats and protocols across systems hinder effective data exchange.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring data security and privacy while sharing across platforms can be complex, especially when dealing with sensitive information about patients or customers.

Future of Data Management Markets
How to Achieve Data Interoperability
To successfully implement data interoperability, organizations should consider basing their approach on the following best practices:
- Adopt Standard Protocols: Use standard data formats (like XML or JSON) and communication protocols (like REST APIs) to facilitate data exchange. Doing this at the outset will save you considerable time down the road since you won’t need to allocate data management resources to “translate” data from different source systems or build cumbersome workarounds to send data where it needs to go.
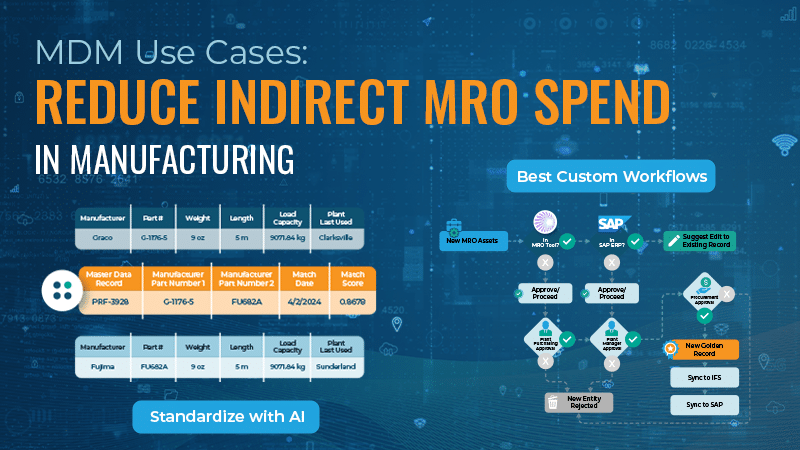
- Investing in an Intermediate System: Deploy intermediate solutions that enable different systems to communicate and share data effectively. Depending on the approach you’re taking, this could be an ETL tool, a master data management (MDM) tool or something else.
- Data Mapping: Build a to determine how your organization will structure its data and then create a data map to instruct data where to go when it’s shared with other systems.
- Collaboration Across Departments: It’s easy for departments to fall into the trap of being protective of their data when it comes to sharing it with other parts of the business. Foster a culture where departments prioritize data sharing and collaboration.
How to Test If Your Data is Interoperable
You can check to see if your data is interoperable by first checking for integrations with the different source systems you need to work with. Most major business software tools come with some out-of-the-box integrations, but for those that don’t, you may need to build them yourself. Workflow automation tools like Zapier may also be an option.
Once you have a way to share data with other systems, validate that it’s working as it should. Specifically, make sure that data from other systems arrives intact and is formatted correctly. In some cases, you may be able to check this yourself, but it’s usually best to ask the people who use the system consistently if they’ve encountered any data issues since incorporating data from other systems.
Data Interoperability Best Practices
After you’ve successfully implemented data interoperability for the systems that need it, there’s still maintenance work to be done to ensure data sharing between systems continues running smoothly. This may look different from organization to organization, but in general, consider these best practices for ensuring data interoperability:
- Continuous Training: Software systems change. Team members come and go. Business needs evolve over time. Try to anticipate these variables by equipping teams with the necessary skills to manage and utilize interoperable systems effectively.
- Regular Audits: Regularly audit data processes to ensure they meet interoperability standards. Integrations can break or become outdated, and human error can cause accidental breakdowns between how various sources share information.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve stakeholders from across the organization to maintain alignment on data goals. It’s especially important to consider whether the organization’s data strategy still serves the needs of the business and delivers real value. Without regular check-ins and course corrections as needed, business leaders might start wondering what value data management brings to the table.
How Data Interoperability Impacts Different Industries
Finance
In finance, data interoperability provides a consolidated view of financial data across multiple platforms, enabling firms to offer personalized services, better protect their customers’ privacy and comply with rigorous regulatory standards.
Healthcare
For healthcare, interoperability can drastically improve patient outcomes by ensuring healthcare providers have access to comprehensive patient records, regardless of where care is received. Many healthcare organizations also rely on data interoperability for provider credentialing.
Government
Government agencies benefit from data interoperability by improving inter-departmental collaboration, increasing transparency, and offering citizen services more efficiently.Manufacturing
In manufacturing, interoperable data supports supply chain optimization, real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, resulting in enhanced productivity and reduced downtime.Tap Your Data’s Full Potential with Profisee
Data interoperability is not merely a technical requirement but a strategic enabler for organizational success across various industries. By overcoming challenges and adopting best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data to drive innovation and gain competitive advantages.
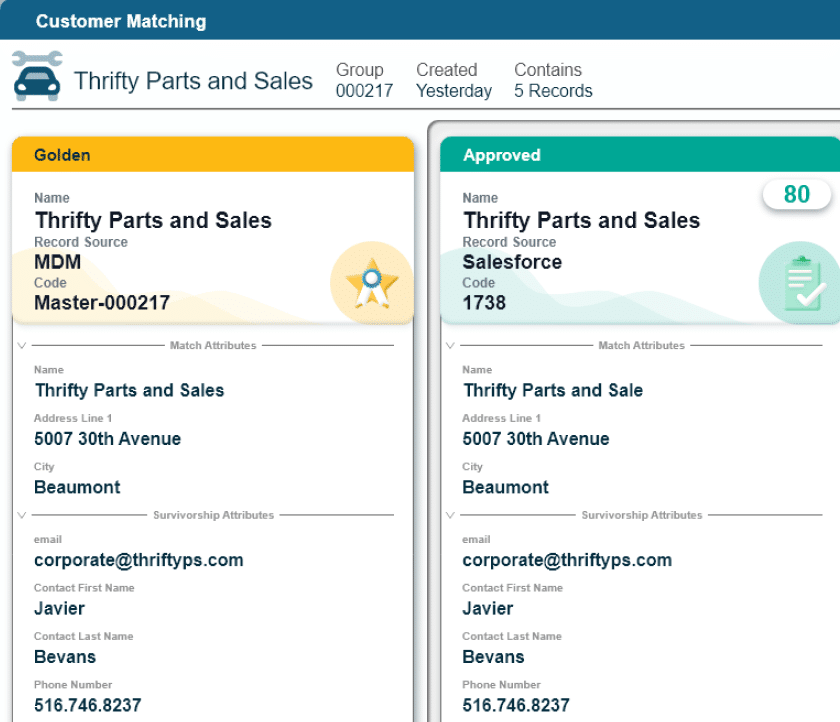
Profisee can help your organization make the most of interoperable data with its best-of-breed master data management platform. Using Profisee MDM, organizations can integrate data from any source, match and merge similar data records, remove duplicate records and standardize data according to their data governance policies.
Downstream systems can access newly created golden records from Profisee, ensuring users always have access to the most up-to-date, complete, accurate and trustworthy data. To learn more about how Profisee can help you with the challenges your organization is facing, explore our Platform page for a more detailed look at how Profisee works with your master data.
See the Benefits of Modern MDM

Forrest Brown
Forrest Brown is the Content Marketing Manager at Profisee and has been writing about B2B tech for eight years, spanning software categories like project management, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and now master data management (MDM). When he's not at work, Forrest enjoys playing music, writing and exploring the Atlanta food scene.