Table of Contents
- What Is Customer Master Data?
- What Are Common Data Sources for Customer Master Data?
- What Is Customer Master Data Management?
- Why Is Customer MDM Important?
- Customer Master Data Management Best Practices
- Customer Data in the Context of Multidomain Master Data Management
- How to Integrate Customer MDM With Your Data Management Systems
- Master Your Customer Data With Profisee MDM
Understanding your customer base can significantly differentiate your business from competitors. For organizations looking to get a better idea of what’s important to their customers, effective customer master data management (MDM) is crucial to achieving a comprehensive Customer 360 view. In this article, we’ll walk you through the essentials of customer MDM, highlight its importance and share best practices to maximize your data management efforts.
What Is Customer Master Data?
Customer master data refers to the unique, unchanging, non-transactional information that identifies and describes a customer within your database. This includes but is not limited to unique identifiers such as names, contact details and demographic data.
It’s important to understand how this differs from transactional data, which records the interactions a customer has with your business, such as purchases or support cases. Master data provides the foundation for building detailed customer profiles, which are critical for personalization and strategic decision-making, when accurately stitched together with transactional data for enterprise analytics, AI use cases and more.

Accelerate Microsoft Fabric Success
What Are Common Data Sources for Customer Master Data?
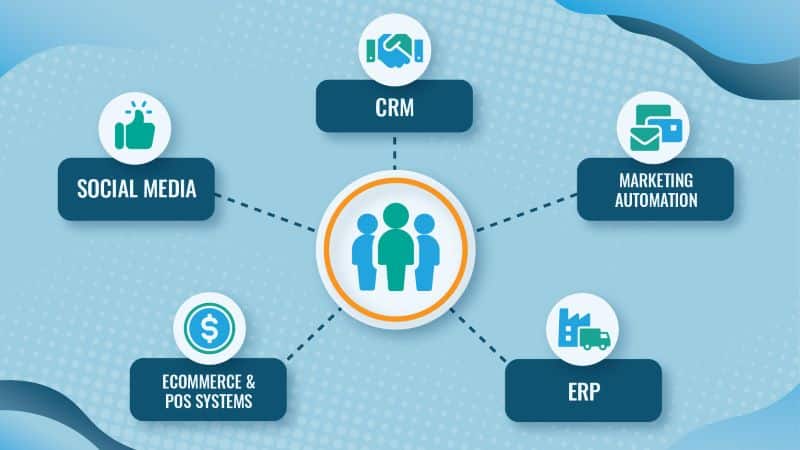
Customer master data can originate in multiple different systems. For larger organizations, the list of source systems for customer master data can grow to be quite long, but in general, most businesses source customer master data from commonly used tools, like CRM and ERP.
As with any data source, it’s imperative to discern which data is master data and which is not. Some examples of customer master data source systems and the master data you might extract from them include:
| Source System | Example Systems and Function | Master Data Examples |
|---|---|---|
| CRM Systems | Systems like Salesforce, HubSpot and Pipedrive capture vital customer interactions and relationship data, like deals closed and pipeline sources | Name, primary address and date of birth |
| ERP Systems | Systems like SAP, Dynamics 365 and NetSuite record information about customers such as their names, billing and shipping addresses, payment methods and purchase history | Company name, billing address and tax ID |
| Marketing Automation Platforms | Marketing automation tools like Marketo and Pardot record valuable information on customer engagement and preferences, but they can also capture customer information through lead forms | Name, email address and segmentation data (e.g., customer, partner, prospect) |
| Ecommerce and POS Systems | Ecommerce tools like Shopify or Salesforce Commerce Cloud and point of sale (POS) tools like Square or NCR can also capture customer information | Name, primary address and loyalty program data |
| Social Media Platforms | Social media platforms like TikTok and LinkedIn can provide valuable demographic and psychographic data about your audience, but determining which of this data is master data is not as black-and-white as it is with other systems. Certain demographic information (such as college-educated) about customers might be considered master data, but it ultimately boils down to what specifically your organization decides to label master data | Profile ID and certain demographic data like age, race and education |
Integrating these diverse data sources helps in compiling a comprehensive and unified view of each customer.
What Is Customer Master Data Management?
Customer Master Data Management (MDM) involves the processes, policies and technologies employed to consistently define and manage core customer data. As with any other data domain, MDM is both a technology and a discipline, referring both to the actual human labor of matching, merging, deduplicating and standardizing data records as well as the software that makes this possible.
Customer MDM ensures data accuracy, consistency and accessibility across the organization, giving relevant downstream systems access to accurate, up-to-date, trustworthy master data for uses like business intelligence (BI) or AI enablement. By implementing customer MDM, businesses can execute several strategic initiatives, like running more targeted marketing campaigns, improving customer service and making more informed decisions.
Why Is Customer MDM Important?
Customer MDM is important for many reasons, but most organizations implement it because it’s a crucial first step for launching a Customer 360 initiative. Customer 360 provides organizations with a unified view of all their customer data, which can provide benefits such as:
- Identifying Profitable Customers: With Customer 360, organizations can analyze and segment customers based on profitability and lifetime value, helping them identify which customers are the most valuable over time.
- Building Personalized Experiences: Access to a single source of truth of accurate, trustworthy data gives organizations more insight into individual customer needs and preferences, helping them better tailor shopping experiences by recommending products or offering discounts.
- Creating Enhanced Marketing Campaigns: Enriched customer data gives marketers more insights about what products customers are interested in, where and how they prefer to shop and when they’re most likely to buy, helping marketers create more targeted marketing campaigns to influence purchasing behavior.
- Improving Demand Forecasting: Analyzing customer trends and behaviors over time helps organizations better anticipate fluctuations in demand for different products and services.
- Boosting Operational Efficiency: Customer 360 also helps organizations streamline their data management processes, reducing redundancies, and human error while widening access to the information that different teams and departments need without bottlenecks.
Customer Master Data Management Best Practices
An MDM program for your customer data should follow the same best practices for master data management in general but with some extra considerations for handling sensitive customer information. For the best results with your customer MDM program, stick to these best practices:
- Implement Data Governance: MDM and data governance go hand-in-hand. Data governance creates the rules that hold data to the standards you set for defining high-quality data, and master data management enforces those rules. Establishing clear data governance policies will help you maintain data quality and compliance and will set you up for future success with MDM.
- Determine a System of Reference and Enable Access: Whether you intend to push golden records from your MDM tool back to your source systems or to a centralized repository like a data warehouse, make sure the downstream systems that need access to your customer master data have it.
- Practice Data Quality Management: Customer MDM is not a one-and-done process. To maintain the accuracy, trustworthiness and quality of your data, it’s important to regularly validate and cleanse data from your source systems.
- Check Integration Capabilities: MDM tools like Profisee support integrations with most third-party systems through APIs, but not every MDM tool does. Determine regular intervals to check that the integrations your organization needs to function are working with your MDM platform and that data is being shared correctly.
- Ensure Security and Privacy Compliance: Implement data protection policies to maintain compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA and work with your organization’s legal and compliance teams periodically to see if you need to update them as the regulatory landscape evolves.
- Conduct User Training and Monitor Adoption: Educate and train staff on MDM tools and processes to encourage widespread adoption and proper usage. The critical piece here is helping people make the connection between MDM and business outcomes. MDM isn’t just about having quality data for quality data’s sake — it’s ultimately about driving positive business outcomes like increasing revenue and improving customer satisfaction.
Customer Data in the Context of Multidomain Master Data Management
No domain exists in a vacuum; the others provide necessary context on how your company should best serve your existing customers. For instance, financial services companies should know where customers purchased products, what channels were used, their payment history and other factors like their risk scores and claims history for a comprehensive, 360-degree view of them.
This requires taking a multidomain approach to master data management that takes a holistic view of product, asset, location or other data in addition to customer data. Customer 360, then, is just a piece of the puzzle when it comes to managing your company’s data estate and leveraging it as a source of competitive advantage. While your immediate problem may include the lack of a unified customer view and the inherent challenges that come with that — like knowing your most profitable customer — you will need to manage your product, supplier, asset or location data. And you need a platform that can scale up with your needs.
How to Integrate Customer MDM With Your Data Management Systems
As I mentioned earlier, MDM tools like Profisee can connect to almost any data source thanks to their combination of native, pre-built integrations and API integration support, but not all tools can.
Once you’ve established that the MDM tool you’ve chosen meets your organization’s needs for data interoperability and can scale with your organization as it grows, take the following steps to keep data accurate, secure and intact as it flows where it’s needed.
- Data Mapping: Map data fields across different systems to ensure consistency and compatibility. Different systems may store the same kinds of data in slightly different ways, so data mapping works as a kind of translator for data between systems.
- Automated Workflows: Develop automated workflows for data synchronization and updates to minimize manual intervention. MDM tools like Profisee often come with workflow automation features, but double-check to make sure your MDM tool can handle this.
- Continuous Monitoring: Software changes all the time, so it’s a good idea to implement monitoring frameworks to track data quality and integration performance.
By following these steps, you can create a unified and efficient data ecosystem that maximizes the potential of your customer master data.
Master Your Customer Data With Profisee MDM
Customer master data management is integral to unlocking the full potential of your business’s data assets, leading to more informed decisions and enhanced customer experiences. By implementing the best practices outlined in this article, your organization will be one step closer to achieving a complete Customer 360 view and staying ahead in the competitive landscape.
Following customer MDM best practices is important, but having the right MDM tool for your project is just as important. Profisee MDM has powerful features like advanced matching and survivorship, relationship management, data governance and workflow automation as well as integration support for all the tools you already use.
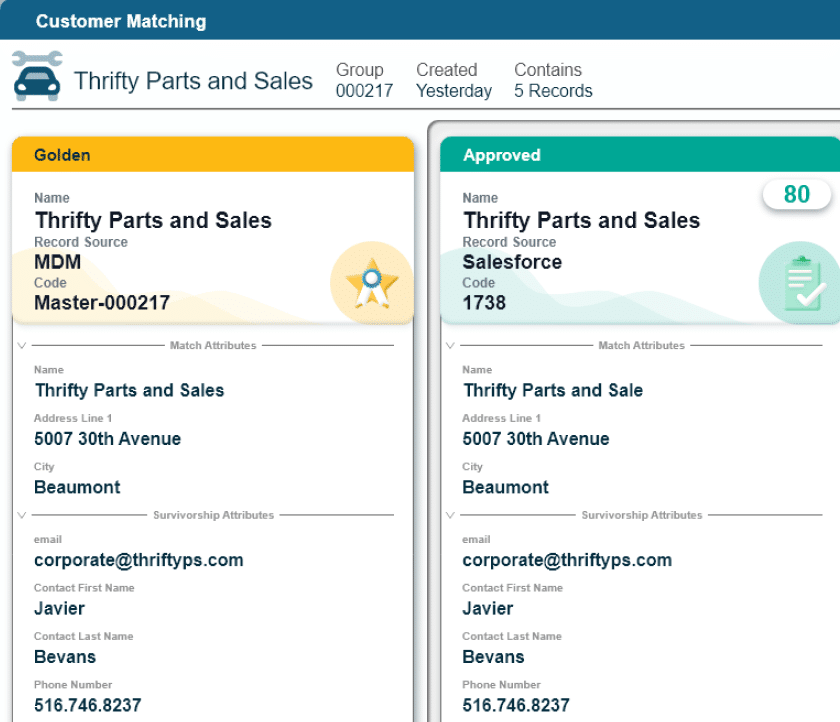
Ready to see how Profisee MDM can transform your data management strategy? Explore how the Profisee platform handles matching and survivorship today and discover how Profisee makes managing your customer master data easy.
Market-Leading Matching Engine

Forrest Brown
Forrest Brown is the Content Marketing Manager at Profisee and has been writing about B2B tech for eight years, spanning software categories like project management, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and now master data management (MDM). When he's not at work, Forrest enjoys playing music, writing and exploring the Atlanta food scene.