Key Takeaways
When customer data is split across retail, commercial and ancillary platforms, banks lose visibility into total relationships, risk exposure and opportunity.
MDM isn’t a replacement for core systems. Rather, it provides a governed layer that reconciles customer records, models relationships and creates a shared foundation across the bank.
Unified customer data shortens onboarding, improves risk assessment and gives teams a reliable basis for analytics and relationship management.
Banks are not short on data. They’re short on coherence.
Customer information is spread across retail systems, commercial platforms, CRMs, lending tools and third-party sources. Each system does its job well enough on its own, but none of these systems are designed to represent the full customer relationship across the bank.
I recently led a webinar focused on this exact challenge. The goal was not to talk about master data management in abstract terms, but to look at how banks can use MDM to solve very specific, very common problems around customer visibility, risk and operational efficiency.
Why Customer Visibility Breaks Down in Banks
Most banks are organized by product and line of business. That structure makes sense operationally, but it almost guarantees fragmented customer data.
Retail and commercial banking typically run on separate cores. Legal entities, individuals, households and officers are modeled differently depending on the system. Over time, each platform develops its own version of the customer, with no reliable way to reconcile those views.
As a result, answering straightforward questions becomes unnecessarily difficult. What is our total exposure to this customer? How are these entities related? Where does this individual show up across the bank?
Without a shared data foundation, those answers are pieced together manually, often under time pressure and rarely with full confidence.
Where Unified Customer Data Creates Real Value
In the webinar, I focused on three areas where banks consistently see impact when customer data is unified and governed properly.
1. Understanding Risk Across the Entire Relationship
Risk assessment depends on understanding how customers and entities are connected. That includes parent and subsidiary relationships, officers and guarantors and the overlap between personal and commercial accounts.
When those relationships are fragmented, risk exposure is understated. Decisions are made based on partial information, and scenario modeling becomes less reliable.
A master data management platform allows banks to explicitly model these relationships and view risk in aggregate. That gives risk teams a more accurate foundation for assessing exposure, running scenarios and supporting lending decisions.
2. Improving Corporate Onboarding and Due Diligence
Corporate onboarding remains highly manual at many banks. Data is gathered from multiple sources, reconciled in spreadsheets and reviewed repeatedly to ensure required diligence has been performed.
This process is time-consuming and error-prone, and it creates frustration for both customers and internal teams.
By centralizing customer data and incorporating third-party enrichment, MDM helps automate large portions of this work. Teams can see what data is complete, what is missing and what has been verified. That shortens onboarding timelines, improves documentation and reduces operational risk.
3. Gaining Visibility Across Retail and Commercial Silos
It is still common for banks to manage retail and commercial customer data entirely separately. In practice, many customer relationships span both environments.
Without a way to connect those systems, banks lack a reliable view of the full relationship. That limits their ability to understand total exposure, identify cross-sell opportunities or manage relationships strategically.
MDM provides a way to link these systems without replacing them. It creates a governed, shared customer record that connects individuals, businesses and households across the bank.
What This Looks Like in Practice
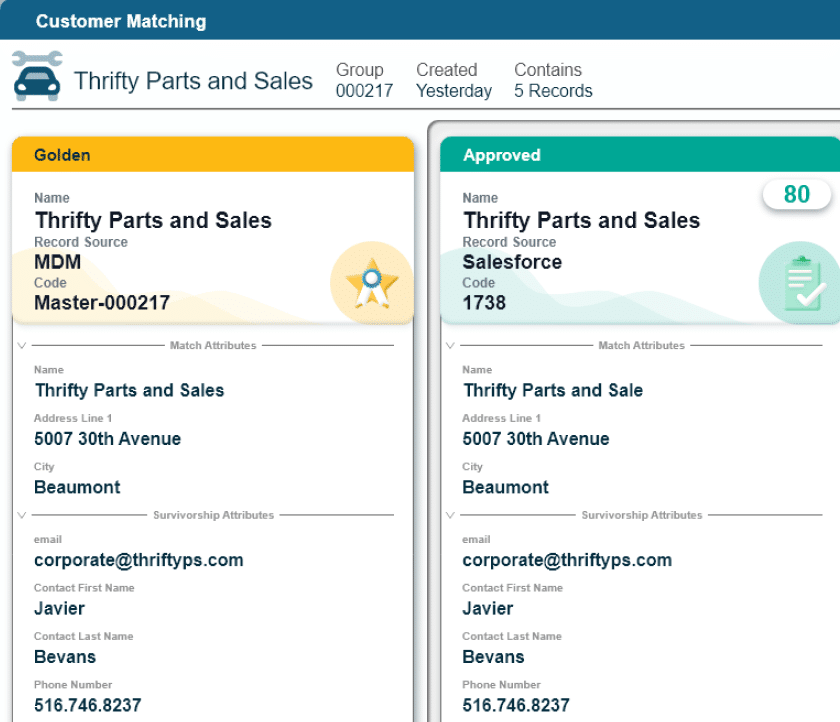
During the session, I walked through a hypothetical example involving a customer with records spread across multiple systems, each with slight variations in name and attributes.
Using MDM, those records are matched and resolved into a single, trusted customer record. External data sources are used to validate and enrich key attributes. From there, related individuals, households and business entities are connected to provide a complete view of the relationship.
This approach allows the bank to understand not just who the customer is, but how they are connected, what products they hold and where risk and opportunity exist across the relationship.
Operational and Business Outcomes
When banks establish a unified customer data foundation, the effects show up across the organization:
- Onboarding processes become more consistent and efficient
- Risk assessments are based on a clearer understanding of relationships and exposure
- Analytics and reporting improve because they are built on reconciled, governed data rather than system-specific extracts
Perhaps most importantly, teams spend less time reconciling data and more time using it.
Eliminate Fragmented Data with MDM
Unifying customer data does not require replacing core systems or forcing every team onto a single platform. It requires a data layer that connects existing systems, governs customer definitions and makes relationships visible across the bank.
Master data management addresses that need directly. It provides a practical way to bring structure to fragmented customer data and support better decision-making across risk, operations and growth.
For a deeper look at these use cases and how banks are applying them today, watch the on-demand webinar.

Christopher Dwight
Christopher is a well-respected master data management (MDM) thought leader and the VP of MDM Strategic Programs at Profisee. Christopher has been in the enterprise information management and MDM space for more than 25 years, including senior leadership stints at Oracle and Informatica. Over those years, Christopher has engaged with hundreds of organizations to assist them in their data management strategies and MDM journeys.