Table of Contents
- What Is Master Data Maintenance?
- Why Do You Need a Master Data Maintenance Process?
- Master Data Management vs. Master Data Maintenance: Key Differences
- Key Steps in the Maintenance Process of Master Data
- 5 Master Data Maintenance Best Practices
- Common Challenges of Master Data Maintenance
- Monitor and Maintain Your Master Data with Profisee
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
Master data maintenance is the ongoing process and set of practices that keeps master data usable and reliable.
Master data maintenance processes include similar steps as those required to build master data, with the addition of data auditing, monitoring and refinement.
A robust master data management solution like Profisee can simplify and speed the creation and maintenance of master data with automated workflows and approvals, strict adherence to data governance standards and clear audit trails for compliance.
In order to preserve the high data standards your team has achieved with your master data management tools, you must put master data maintenance plans into place.
With the millions of data points created or changed within a typical workday, master data can begin to degrade as soon as it’s established. And when 69% of companies report that bad data hampers their ability to make good decisions, having consistently reliable data is a competitive advantage.
Neglecting maintenance practices could lead to confusion, miscalculations, revenue loss or even the need for costly large-scale data projects to restore data quality. This article will guide you through the importance of and best practices for maintaining the quality and usability of your master data.

Accelerate Microsoft Fabric Success
What Is Master Data Maintenance?
Master data maintenance is the daily practice and behaviors required by the organization to conserve the quality and usability of the company’s master data. Master data maintenance should start immediately after the establishment of golden records. Every member of the team is responsible for maintenance. However, data stewards and the company’s data professionals take responsibility for the level of master data usability across the organization.
Why Do You Need a Master Data Maintenance Process?
Companies must practice continual maintenance as part of daily work in order to keep master data in a usable, compliant and reliable state. Due to its changeable nature, companies that use data without maintaining it will inevitably degrade the reliability of that data through inadvertent means like manual entry in source systems and oversights in data processing. According to Data Science Central, data decays at a rate of 30% per year, a rate that can quickly spiral out of control. In extreme cases, third-party bad actors may further reduce the quality of data through breaches and malware.
A healthy master data maintenance practice means the company will:
- Prevent data decay and obsolescence by ensuring that master databases contain the most up-to-date data.
- Sustain compliance readiness by keeping continuous logs and audit trails that the team can quickly pull for compliance checks.
- Minimize duplicate and conflicting records by consistently running data cleansing and updates.
- Keep integrations running smoothly by checking APIs, webhooks and other connection types to ensure they’re in working order.
- Maintain trust across departments through consistent records that ease communication.
- Reduce long-term remediation costs through continual, small-scale updates and changes rather than expensive, sweeping projects that stall operations.
A healthy master data maintenance practice that becomes part of the day-to-day operations saves the company time and money while improving communication and data consensus.
Master Data Management vs. Master Data Maintenance: Key Differences
Master data maintenance is the ongoing, hands-on discipline that keeps master data reliable long after initial implementation. That practice includes careful monitoring of the systems that support master data like an MDM solution, APIs, databases, and source software that is typical to business like CRM and finance software, or specialized software like supply chain master data management solutions. It also requires the entire organization to work in a way that supports data reliability by using automation and following manual processes exactly as defined.
Master data management is the overarching set of practices and frameworks that creates and maintains master data within the organization. It begins with investigating how master data needs to work within the company for optimal efficiency and incorporates master data maintenance after master data has been created.
| Characteristic | Master Data Management | Master Data Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Key intent | Plan, create, and manage data quality | Sustain data quality for the lifecycle |
| Scope | Overarching process that includes planning, implementation, operations and maintenance. | Begins after master data has been created. Designed to preserve and improve data quality |
| Responsible parties | IT, data | Entire company |
| Key Technology | Source systems, analytics, APIs, MDM, databases | Source systems, analytics, APIs, MDM, databases |
Key Steps in the Maintenance Process of Master Data
Maintaining master data within an organization is a complex mix of auditing, cleansing, integration, validation, monitoring and retirement that happens near simultaneously once the organization has a mature master data management process in place. However, you can begin maintenance tasks by following these key steps.
1. Identify and Collect Master Data Sources
Work with all company departments to identify all sources of master data. A thorough search at this stage will prevent data discrepancies created by siloed or otherwise inaccessible data buried within departmental sources.
2. Validate and Standardize Data Inputs
The second step requires the team to analyze data inputs to verify their validity. At this stage, check that data inputs are up-to-date and that they are actually used by anyone in the company. Further, standardize data inputs by deciding what data entities and records teams need in the course of business and what format those records should take. For example, standardization may combine two fields of [firstname] [lastname] into a single field [lastname, firstname]. These decisions should be based on business needs rather than stakeholder personal preference, as they will populate data throughout the company.
3. Enrich and Consolidate Data Records
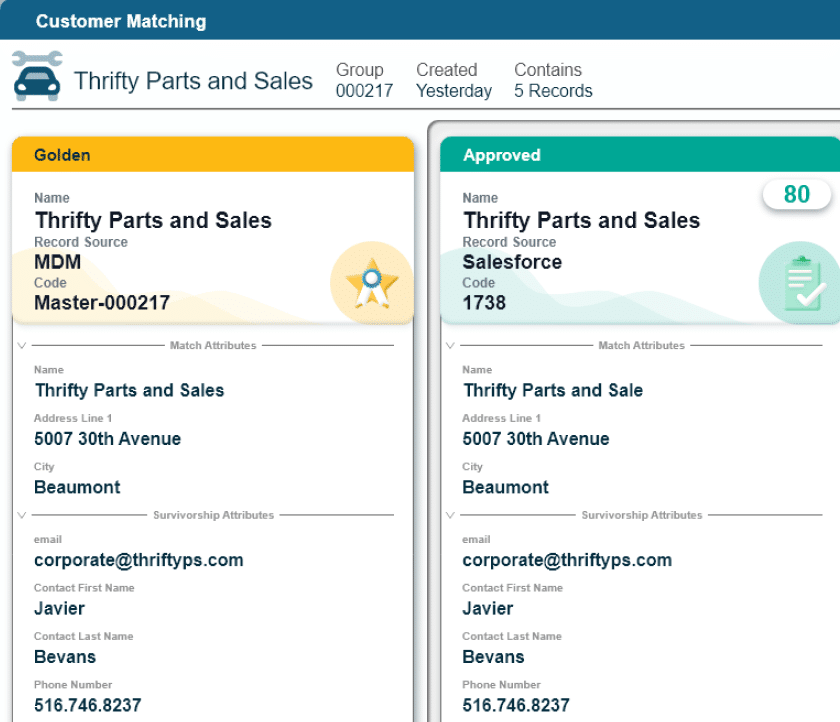
Once you validate data inputs and standardize formats, begin the process of consolidating and enriching records by combining, deduplicating and cleansing the data and augmenting any missing records with data from third-party verification systems. Using automated systems to perform data matching and de-duplication, and AI-supplemented software to perform more complex functions like fuzzy matching and record augmentation will add speed and accuracy to this process.
4. Integrate Data Across Systems and Applications
Master data maintenance is a two-way street: you pull data from source systems to create golden records, then you populate those records back into source systems and across company applications. Re-populating all company systems with the golden records is important because it:
- Ensures everyone is using the same set of records
- Improves analytic consistency
- Provides a visible template for entering new records
5. Review and Approve Data Changes Through Governance
Once golden records have populated throughout the company software, it’s time to lay down the (data) law by implementing master data governance across the company. Changes will need to be made to data formatting, source connections or technology, but each of these changes should follow a defined (and automated) approval process. When the process is defined, it promotes uniformity for all decisions, keeping the full scope of data use in mind and not making allowances for individual departments or employees that might affect overall data reliability.
By automating master data management approval processes, each decision can take hours or days rather than weeks or months, keeping data moving at a speed that helps the business instead of slowing it down.
6. Synchronize and Update Data in Real Time
Data updates from source software should move just as fast as approvals. Real-time data updates that populate across the company source software quickly ensure that everyone makes decisions according to the latest data. A robust MDM software with automatic sync that works according to the company’s governance rules means the data team can focus on improvements to the overall system, rather than manually syncing and updating data to the latest versions.
7. Audit, Monitor, and Refine Data Quality Regularly
After initial processing, this step becomes the daily work for data professionals. Audit data by performing manual and automated checks on data sets to ensure they fit governance rules and provide the needed insights for business units. Monitor processes to keep APIs connected, source systems exchanging data with the MDM software and check with business units to double-check they follow the latest guidance for data entry. As you perform audits and checks, note any inconsistencies and issues against the KPIs you set for MDM measurement and showing value of the project. Then meet again with the data quality stakeholders to formulate new governance rules and data processes to address those issues and restore the high level of data quality you need.
5 Master Data Maintenance Best Practices
Maintaining scalable master data quality in the long term is a big job. These actionable master data management best practices will help you avoid common pitfalls and prepare the team to tackle the complex and changing landscape of business master data. Use these best practices alongside Profisee’s 6 pillars for MDM success.
1. Prioritize High-Value Data Domains First
It’s tempting to want to fix everything all at once, but start small and scale once your team has figured out what works. Begin with the domains most closely tied to revenue, compliance or customer experience as these will have the biggest impacts on revenue or business operations. Look especially to build master data golden records for domains that do not change often, like vendor master file and supplier information management systems. Once you prove the success of your master data maintenance campaign you can scale to other domains.
2. Balance Centralized Standards With Local Flexibility
It’s tempting to try to force all business units into uniform standards across the board to make things simple. But business is complex, and that complexity multiplies as companies expand to different regions. The data team must learn to balance global rules with regional adaptations needed for clarity, hierarchy or compliance purposes. A bit of local flexibility will lead to wider compliance with governance needs.
3. Build a Data Stewardship Network Across the Business
Data stewardship is everyone’s responsibility. Work with all departments to train employees on new processes and identify data quality maintenance needs as they arise. Finance, marketing, revenue, sales, manufacturing and operations — they all have a stake in quality data. In the retail industry alone, there was an estimated $1.77 trillion difference between expected and actual stock levels, differences that reliable and usable product data could offset. When you go beyond IT and bring other departments into the conversation, you can better keep data aligned with the actual business use cases.
4. Automate Routine Maintenance but Keep Human Oversight
We’re not ready to give everything up to the machines yet. Leverage automated and AI tools for deduplication, enrichment, and monitoring, but assign humans to resolve exceptions and disputes. An exception resolution team of departmental stakeholders and business data users will help the data team align with business needs and build governance that works to improve company operations.
5. Track and Share Data Quality Metrics Transparently
Finally, make the data quality project’s progress visible to the company. Report accuracy, completeness, and timeliness scores so leadership can see ROI and teams stay accountable. It may feel repetitive to the data team because they live in the data every day, but consistent repetition and updates will help other business units remember the importance of compliance and reinforce the value of high-quality and usable data.
Common Challenges of Master Data Maintenance
Master data maintenance projects bring inherent complexity due to the need to build company-wide consensus. In addition to the complexity of the initial master data project, challenges like silos, lack of standards, duplicates and more can affect progress. The table below details the impact of these challenges and how people, process, and technology solutions resolve them.
| Master Data Maintenance Challenge | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Data silos | Inconsistent data, reporting and analytics. | Work with all business units to incorporate existing software. Consider updating legacy systems to those that integrate directly with MDM and reduce manual processes. |
| Lack of data standards | Inconsistent data, degrading quality, departmental and individual movements away from agreed-upon levels of quality. Compliance issues and inaccurate reporting. | Document and enforce data governance through MDM and data governance rules. |
| Duplicate data | Compliance issues, inaccurate analysis and forecasts, confusion. | Use automated systems to cleanse and de-duplicate data as it is ingested by the MDM platform. |
| Poor quality data | Compliance issues, inaccurate analysis and forecasts, confusion, revenue decrease, operational slowdowns | Define and document quality standards and enforce through governance. Use MDM augmented with AI and automation as a hands-off approach to data quality maintenance. |
| Lack of company buy-in | Lack of compliance with governance and data processes, which leads to degraded data, loss of revenue and operational slowdowns. | Communicate with stakeholders, make them part of the process, discuss real-world business use cases for data. Communicate success and complications, ask for support and show business impacts of all projects. |
Monitor and Maintain Your Master Data with Profisee
Master data maintenance is everyone’s responsibility, and a master data management platform with built-in automations, integrated governance and AI-driven cleansing technology can help your company build and preserve master data that makes your company move faster. Profisee master data management solution makes it easy to integrate master data best practices into the company’s daily business processes.
Request a demo to see Profisee’s modern master data maintenance and management in action.
Frequently Asked Questions
Maintenance master data file vs. master data maintenance: Are they the same?
No. A maintenance master data file is a collection of master data related to company assets that require maintenance. Example records found in a maintenance master data file are:
- Records for the company-owned fleet of vehicles including license plate numbers, VIN numbers and insurance data.
- Serial numbers, contact information and repair schedules for machines within a hospital system.
Master data maintenance is the practices and technology that preserve the reliability and usability of master data during the course of business use. Master data maintenance includes:
- Technology including source data systems, MDM software, databases, and API connections.
- Data governance rules and standards.
- Monitoring and auditing of connections and data quality.
What is master data maintenance in SAP?
Master data maintenance in SAP is the same as master data maintenance in other technologies except that it employs SAP systems like SAP data governance and SAP master data management.
Which tools can I use to automate master data maintenance?
Automated master data maintenance can be achieved through:
- Automated and AI-assisted data matching and cleansing
- Integrated data governance
- API and integration monitoring
- Audit logs
- Exception-based error visibility
Profisee MDM includes these features and more that drive data quality and usability at scale.
What types of master data should I maintain?
Companies should maintain master data across the domains that drive core business operations. Common master data domains many companies maintain include:
- Customer 360 information including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses
- Product descriptions, sizes, SKU numbers, and vital statistics.
- Vendor data including company names, contact names, addresses, phone numbers
- Location-specific data for franchise, vendors, customers and company branches
Types of master data your company maintains depends on industry and company need, and may evolve over time as the company grows.
What would happen if I neglect master data maintenance?
Neglecting master data may cause negative business outcomes, including:
- Confusion among business units
- Breakdown in communication between business units
- Inaccurate forecasts and estimates
- Slowed business operations
- Lack of trust among vendors and customers
What roles are typically involved in master data maintenance?
The roles involved in master data maintenance span the business, including:
- Data owners: The parties ultimately responsible for the quality and usefulness of data across the business. Data owners often sit within the Data or IT departments, as they require specialized knowledge of databases, analysis and integration.
- Data stewards: The individuals across the company are responsible for following governance rules, training business users and calling attention to data quality problems.
- IT and data departments: These professionals maintain the processes and connections that support data quality, including choosing appropriate technology and maintaining API connections.
- Business data users: Business data users should be highly involved in the process of planning, and should use their position as end-users to help data professionals monitor data quality.
What’s the impact of poor master data maintenance on business performance?
Poor master data maintenance can result in:
- Operational slowdowns due to confusion and degraded data
- Confusion and inaccuracies in reporting, forecasting and analysis
- Failure to meet regulatory and compliance requirements
These business performance issues can greatly impact revenue growth, trust with customers and vendors and brand performance in the marketplace.

Tamara Scott
Tamara Scott is a writer, editor and content strategist with over a decade of experience located in Nashville, TN. Tamara holds a Master's in English from Belmont University, formerly served as Director of Content for TechRepublic, and her work has appeared in ServerWatch and EPI-USE.com, among others. When she's not crafting SEO-informed and conversion-ready content for SaaS and IT service companies, she's probably at home on her pottery wheel. Connect with her on LinkedIn.