Key Takeaways
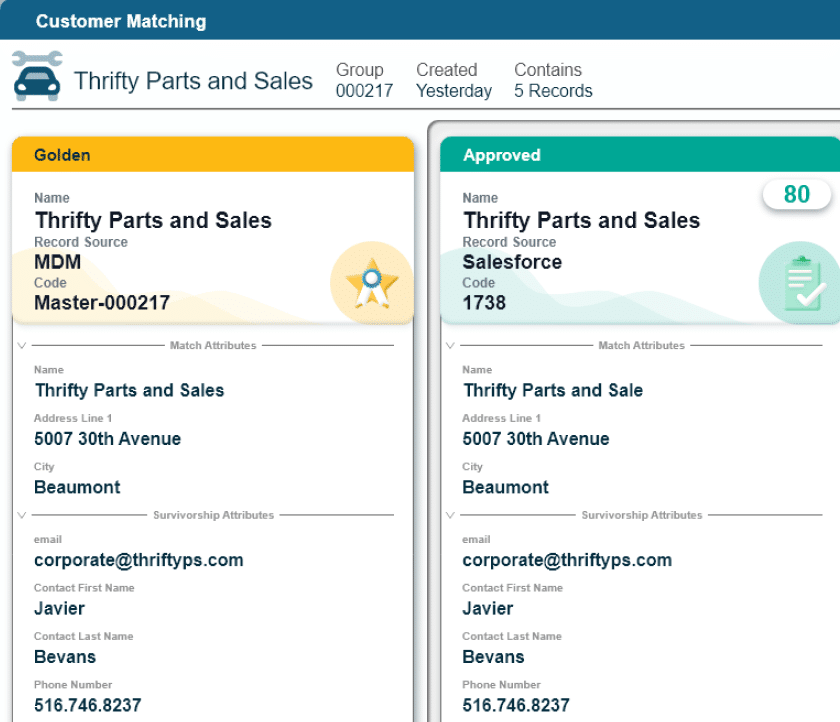
MDM survivorship rules determine which attribute values populate your golden record when you have multiple, inconsistent records about the same entity.
Effective survivorship strategies combine multiple techniques tailored to each attribute’s business requirements.
Proper master data survivorship uses intelligent automation to improve compliance, operational efficiency and customer experience while reducing manual data stewardship.
Profisee’s survivorship functionality provides attribute-level configuration, multiple rule types and full auditability to help organizations build trustworthy golden records.
MDM survivorship rules govern which data values are saved (or, which ones “survive”) to the golden record in situations where there are duplicate or conflicting values in matching records. Instead of picking one record wholesale to save, these rules tell your MDM tool to look at each attribute within matching or similar records and choose the best option for each attribute.
Poor survivorship rules can cause downstream problems in everything from financial reports to customer service, and a total lack of survivorship rules can lead to untrustworthy, duplicated and inconsistent data. Organizations that build and maintain strong survivorship logic can avoid inaccurate, untrusted master data and instead deliver usable, trustworthy master data that helps drive business results.

Accelerate Microsoft Fabric Success
What Is MDM Survivorship?
MDM survivorship is the set of rules and logic that determines which attribute value is saved to the golden record from a set of competing source records. When an MDM tool identifies multiple records that represent an entity like a customer, supplier or product, it uses survivorship rules to decide which address, contact name or product description is most accurate.
MDM survivorship happens after you match raw data from your source systems and before you make the golden records available to downstream systems. The survivorship rules decide which conflicting and overlapping attributes have the most correct data that should be saved into a single, useful record.
While data matching techniques can identify and cluster similar records across several different sources, MDM survivorship chooses a single winning value for each attribute associated with the golden record.
Why Data Survivorship Matters in MDM
MDM data survivorship makes a difference in how data is used across the organization, as it gives the entire organization peace of mind knowing its data is trustworthy and usable. Consider how the benefits of survivorship rules make a difference across the organization.
Analytics and Reporting
In analytics and reporting, choosing the wrong legal entity name can cause incorrect revenue attribution that throws off executive dashboards and investor communications. For large organizations with complex financial architectures, accurate reporting can make or break funding deals, tax reporting and stockholder confidence.
Customer Experience
Customer experience depends on accurate information that directly affects the company’s bottom line. Survivorship rules ensure that sales and marketing campaign emails make it to the most up-to-date email address rather than an old Hotmail address a customer provided at checkout five years ago. Survivorship rules ensure customer success managers have an account’s complete order data because all orders are saved under a single entity rather than several similar versions spread across three different ERP systems.
Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency relies on accurate data within every operational system. The company risks financial losses for payment delays if bookkeeping sends invoices to the wrong address. Logistics partners need updated addresses and product information for more efficient transfer and warehousing. When vital MDM attributes are missing or confusing, processes can slow down or break at multiple points along a workflow.
Compliance
Compliance requirements have ramifications outside of the boardroom that could result in fines or work delays. If the team trusts an outdated tax ID associated with the right entity name, address or classification, the resulting filing errors may bring hefty penalties and even audits. However, survivorship rules that take into account factors such as data freshness and source authority within a regulatory environment guard against problematic mistakes.
Data Stewardship
MDM survivorship rules also help data stewards be more productive by automating processes that would otherwise need manual review. This frees stewards from spending countless hours trying to determine which records have the right information so they can focus more on getting the business the data it needs for strategic initiatives, like boosting customer cross- or up-sell.
Common MDM Survivorship Rules and Techniques
Effective survivorship strategies make use of several rule types, each suited to different attributes and business contexts. Most organizations build a set of different rules that treat attributes according to their business use and the most authoritative sources. Understanding these techniques can clarify which logic should match data quality requirements.
Source System Priority
Source system priority defines a hierarchy of data sources as the most trustworthy for any given attribute. For example, a source system priority rule may declare that the customer contact name attribute should come from the CRM, while supply chain management software provides location information for all vendors.
This system works best for well-organized or highly regulated organizations that have a clear hierarchy for individual MDM attributes, such as using the company’s tax system as the sole source for tax ID or classification codes.
Most Recent Update
This survivorship method selects the most recently modified value for an attribute and assumes that newer data is more accurate. This rule type works well for data that changes frequently, which may make it less applicable for master data. Attributes like customer addresses, email addresses and phone numbers may benefit from this rule since people may update this data frequently and across several source systems.
Recency-based survivorship should be applied with caution, as it requires reliable timestamp metadata across source systems and an agreed-upon standard for what constitutes a meaningful update. Survivorship rules based on the most recent updates can be thrown off by metadata updates completed in a nightly batch run, for example, which could lead to incorrect information published to the golden record.
Most Complete Record
The most complete record survivorship rule favors the record with the fewest incomplete or empty attributes across all the systems and assumes that the most complete record is also the most accurate. It works well for descriptive attributes like product descriptions or supplementary details and notes where having a value in place is better than none at all.
Due to the high risk of error with completeness rules, they are best used in combination with other techniques that favor recency or on attributes that don’t change much over time.
Data Quality Score
A data quality score technique allows the data team to assign a score for each attribute based on several dimensions including:
- Accuracy
- Completeness
- Conformity to standards
- Consistency across attributes
While more complicated than other rules on this list, a data quality score can combine several different priorities and choose the attribute with the highest score as the one that survives to the golden record. This does require more upfront investment in planning and refining the algorithm, but that investment may pay off in more reliable data.
A company may choose to define a data quality scoring rule to marketing leads sourced from multiple different touchpoints across the marketing funnel. A contact’s email address may score high for accuracy when it comes from the shipping application while that same contact’s email address may score poorly due to validation from the marketing newsletter. However, a different email address that’s associated with an app login may win out because it’s been used consistently for many months.
Conditional Rules
Conditional MDM survivorship rules apply “if-then” logic based on the value or context of the attribute and is best used when survivorship requires defined circumstances or when multiple options can apply depending on location, language or data type.
Some examples of conditional rules include populating different tax numbers based on location or even different data sources for different business sizes. Conditional rules can also extend to business processes by relying on procurement data for the first 90 days the customer is active and then switching to a recency-based rule as the customer and their data populate to more systems.
Hybrid Approaches
Most mature survivorship strategies combine multiple rule types based on need either by defining different rules per attribute or creating a cascading logic that allows the system to fall back on another rule should the preferred attribute not exist or does not meet standards.
A retail organization might use a hybrid approach for product master data by trusting the merchandising system for category and pricing attributes, applying recency rules for quickly-changing marketing campaign data and using quality scoring for supplier-provided attributes with variable data reliability. Hybrid approaches provide the flexibility to define survivorship rules based on business practices.
Best Practices for Survivorship in MDM
Survivorship in MDM requires more than rules. Detailed governance, stakeholder collaboration and continuous refinement all contribute to a successful MDM initiative and smoother business operations. These best practices will keep survivorship logic accurate and reliable.
- Define rules at the attribute-level: Building logic that trusts full records from a single data source like “trust the ERP for all customer data” can quickly lead to problems. Instead, build logic based on each attribute needed for a record: contact name, company name, company address, etc.
- Combine multiple rule types: Multiple rule types that back one another up will ultimately lead to fewer null values and more accurate survivorship. Consider stacking system priority with conditional or completeness rules. Multiple rules set in advance can reduce data steward manual review and increase usability.
- Document rules for transparency: When implementing the rules, they may seem to speak for themselves. But good documentation provides not only what the rule is but why it was decided. Documentation results in faster updates and speedy onboarding for new team members.
- Monitor results with data quality metrics: No data system is a set-it-and-forget-it. Set data quality metrics and KPIs at the beginning of the initiative and hold regular reviews to understand where survivorship rules work and where they fall short.
- Involve business stakeholders in rule definition: Master data is worthless if it cannot be used by the business. Involve business stakeholders including leaders and everyday data users to best understand how data is used in the business and build rules that make that more efficient.
- Review and update rules as systems and priorities change: With every metric and goal review, question what internal systems, priorities and strategies have changed for business users and how the survivorship rules and MDM system as a whole contributes to those. This keeps data aligned with business priorities and keeps the data serving the business.
Strengthen Your MDM Survivorship Strategy with Profisee
Profisee’s survivorship rule engine provides the flexibility and control that complex master data environments demand. The platform supports multiple rule types like source, date, completeness, and customer logic within a single survivorship strategy. The attribute-level survivorship configuration ensures that the most accurate data survives to the golden record. Built in data quality scoring makes it easy to program a quality algorithm that defines the most reliable attribute based on multiple factors. And Profisee comes compliance-ready with auditability and rule change tracking that brings transparency to survivorship that’s ready for iteration.
A national healthcare group used Profisee MDM to integrate four critical domains across several systems and processes cobbled together over business and practice area acquisitions. By applying attribute-level survivorship rules, inconsistent and low-quality data that was copied across multiple systems and impeded critical operations was consolidated across source systems. Provider, patient, payer and location data went from inaccurate to reliable, and the team no longer wastes time manually reviewing and researching untrustworthy data.
See how Profisee’s MDM survivorship capabilities help you choose the right record every time. Request a demo today.

Tamara Scott
Tamara Scott is a writer, editor and content strategist with over a decade of experience located in Nashville, TN. Tamara holds a Master's in English from Belmont University, formerly served as Director of Content for TechRepublic, and her work has appeared in ServerWatch and EPI-USE.com, among others. When she's not crafting SEO-informed and conversion-ready content for SaaS and IT service companies, she's probably at home on her pottery wheel. Connect with her on LinkedIn.